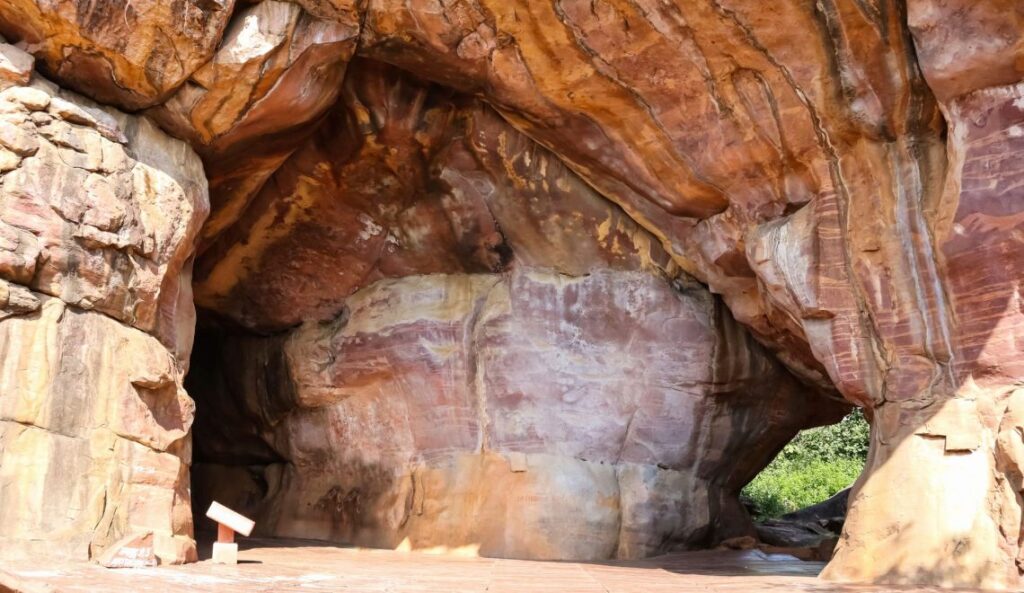
Welcome, fellow time travellers, to a captivating journey back in history of the ancient caves of Madhya Pradesh! In the heart of India lies a treasure trove of ancient wonders waiting to be discovered by the intrepid explorers of today.
Madhya Pradesh, often called the “Heart of India,” is home to a magnificent collection of 11 ancient caves that have stood the test of time, preserving tales of ancient civilizations and artistic brilliance.
Moreover, as we embark on this enthralling adventure, we will unveil the secrets of the past, delving into the architectural marvels, religious sanctuaries, and cultural legacies hidden within the rock-cut chambers.
So, fasten your seatbelts as we embark on a time traveller’s delight to uncover the 11 ancient caves of Madhya Pradesh.
1. Bhimbetka Caves

However, located in the Raisen district of Madhya Pradesh, Bhimbetka Caves are an archaeological marvel that provides a fascinating glimpse into India’s ancient history.
These caves are renowned for their extensive rock art, making them a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Moreover, the name “Bhimbetka” is derived from the epic Mahabharata, with “Bhim” referring to one of the Pandava brothers.
However, the caves date back to the Palaeolithic era and have been inhabited by humans for over 30,000 years. The rock shelters are adorned with intricate paintings and engravings, showcasing prehistoric communities’ lifestyles, rituals, and culture.
These ancient artworks portray scenes of hunting, dancing, battles, and religious ceremonies, providing valuable insights into the early human civilizations that once thrived in this region.
2. Udayagiri Caves

Udayagiri Caves, also known as the Cave Complex of Udayagiri, is a group of twenty rock-cut caves near Vidisha in Madhya Pradesh.
Initially, these caves hold historical and religious significance, representing an amalgamation of Hindu and Jain art and architecture.
The caves date back to the Gupta period, around the 4th and 5th centuries CE. They were carved out of sandstone cliffs and served as monastic retreats for ascetics and religious practitioners.
Furthermore, the architecture of the Udayagiri Caves showcases an impressive fusion of Gupta and post-Gupta styles.
The site is particularly famous for the massive sculpture of Lord Vishnu in his Varaha (boar) incarnation, one of the most remarkable representations of Varaha in Indian art.
3. Bagh Caves

Moreover, situated near Bagh in the Dhar district of Madhya Pradesh, the Bagh Caves are a group of nine rock-cut caves primarily renowned for their exquisite paintings and ancient sculptures.
The caves were created during the Gupta period, around the 5th and 6th centuries CE.
The unique feature of the Bagh Caves is the exemplary use of tempera technique in their paintings, which is a rare occurrence in Indian art history.
Mainly, the colourful murals depict various scenes from Buddhist Jataka tales and the life of Buddha. The paintings’ serene expressions, vibrant colours, and intricate detailing have captivated art enthusiasts and historians alike.
4. Raisen Caves

The Raisen Caves, located on the southern slope of a hill in the Raisen district of Madhya Pradesh, offer an intriguing glimpse into India’s ancient past.
These rock-cut caves, dating back to the 6th to 7th century AD, belong to the Gupta period and are dedicated to Hindu and Jain deities. The site consists of caves, each showcasing distinct architectural styles and religious influences.
The Raisen Caves hold historical importance due to their association with both Hinduism and Jainism. The sculptures and carvings found inside the caves represent various deities and Jain Tirthankaras.
Some caves serve as Hindu temples, while others are Jain shrines. This religious diversity reflects the inclusive nature of Indian society during that era, where different religious communities coexisted and shared spaces.
The Raisen Caves also offer stunning views of the surrounding landscape, making them not just places of worship but also sites of natural beauty and serenity.
Further, the intricate carvings on the cave walls depict scenes from Hindu epics like Ramayana and Mahabharata, along with images of Tirthankaras and Yakshas from Jain mythology.
These carvings are not only artistically impressive but also provide valuable insights into ancient India’s religious beliefs and cultural practices.
5. Pandav Caves

Nestled amidst the lush green forests of Pachmarhi, the Pandav Caves are an intriguing set of rock-cut dwellings shrouded in mythical legends and historical significance. Local folklore claims that the Pandavas, the protagonists of the epic Mahabharata, lived in these caves during their years of exile.
While the connection to the Pandavas remains popular among locals, archaeological evidence suggests that Buddhist monks inhabited the Pandav Caves during the 1st century AD.
However, the caves resemble Buddhist viharas, indicating their association with Buddhist monastic practices.
The location of the Pandav Caves within the Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve adds to their allure, as visitors can experience both historical intrigue and natural beauty during their exploration.
The caves’ architecture, with simple cells for meditation and living quarters, reflects the ascetic lifestyle of the monks who once resided here.
Today, the Pandav Caves serve as an essential archaeological site and a tourist attraction, drawing history enthusiasts, nature lovers, and spiritual seekers alike.
The tranquil surroundings and intriguing historical connections make the Pandav Caves a must-visit destination for those interested in unravelling the mysteries of ancient India.
6. Dhar Caves

The Dhar Caves, also known as Bagh Caves, are an extraordinary group of ancient rock-cut caves in Dhar, Madhya Pradesh, India. People renowned these caves for their exquisite Buddhist architecture and the Gupta period.
There are a total of 5 caves at the Dhar site, each displaying unique artistic styles and religious themes.
The most remarkable feature of these caves is their stunningly detailed murals and sculptures, created by artists to depict various aspects of Buddhist mythology and life during that era.
The skillful craftsmanship evident in the sculptures, ranging from serene Bodhisattvas to intricate floral patterns, leaves visitors in awe of the artistry of the ancient artisans.
Intricate rock carvings. Carving out the cliffs of the Vindhya Range, artisans created the Dhar Caves between the 5th and 7th centuries AD.
7. Jata Shankar Caves

Nestled in the rocky hills of Pachmarhi, the Jata Shankar Caves are a sacred and significant Hindu pilgrimage site in Madhya Pradesh.
We name these natural caves after the unique stalagmite formations that resemble Lord Shiva’s matted locks, known as ‘Jata’ in Sanskrit.
Devotees believe that the caves have religious significance and that the stalagmite formations manifest Lord Shiva himself.
The tranquil atmosphere inside the caves adds to the spiritual ambiance, making it a serene place for meditation and reflection.
The Jata Shankar Caves attract devotees and tourists alike, who witness this awe-inspiring natural wonder and pay their respects to Lord Shiva.
8. Pataleshwar Caves

Pataleshwar Caves, located in the picturesque hill station of Pachmarhi in Madhya Pradesh, India, is a fascinating historical and religious site.
Carved out of sandstone cliffs, these caves hold immense significance in Hindu mythology and architecture.
The caves comprise a complex of five rock-cut shrines dedicated to Lord Shiva, and scholars believe that artisans constructed them during the Gupta period, between the 5th and 8th centuries AD.
The Pataleshwar Caves get their name from combining two words: “Patal,” meaning the underworld, and “Eshwar,” referring to Lord Shiva.
According to Hindu mythology, these caves represent the entrance to the netherworld where Lord Shiva resides.
The intricate carvings and sculptures on the cave walls depict various mythological scenes, including the Trimurti, the trinity of Brahma, Vishnu, and Shiva.
Aside from its religious importance, the Pataleshwar Caves also offer insights into the exceptional architectural skills of the ancient artisans.
The precise and delicate carvings and the skilful interplay of light and shadows create an awe-inspiring ambiance within the caves.
9. Bada Mahadev Caves

In the heart of Madhya Pradesh, the Bada Mahadev Caves feature rock-cut formations dedicated to Lord Shiva.
Historians believe that builders constructed these ancient caves during the Kalachuri period, which flourished between the 10th and 12th centuries AD. The caves near the town of Mandsaur hold historical, religious, and architectural significance.
The Bada Mahadev Caves consist of a large cave temple that houses a magnificent lingam, the symbolic representation of Lord Shiva.
Ornate carvings adorn the temple’s entrance, showcasing tales from Hindu mythology and various celestial beings.
The caves hold a special place in the hearts of the devotees who visit to seek blessings and spiritual solace. The serene environment surrounding the Bada Mahadev Caves adds to the spiritual experience and attracts pilgrims and tourists alike.
10. Chhota Mahadev Caves

Adjacent to the Bada Mahadev Caves, the Chhota Mahadev Caves form a smaller complex of rock-cut shrines dedicated to Lord Shiva.
Like their larger counterparts, these caves also date back to the Kalachuri period, boasting a similar architectural style and religious significance.
Though smaller, the Chhota Mahadev Caves exhibit intricately carved stone sculptures depicting scenes from Hindu mythology.
The craftsmanship and attention to detail highlight the devotion and skills of the ancient artisans who worked on these caves centuries ago.
11. Mandsaur Caves

The Mandsaur Caves, located in the Malwa region of Madhya Pradesh, hold a fascinating historical legacy that dates back to the 6th century AD. These rock-cut caves are a testament to the region’s forts in Madhya Pradesh and have contributed significantly to our understanding of ancient Indian art and architecture.
The Mandsaur Caves, also known as the Pashupatinath Caves, consist of five caves carved out of a sandstone cliff.
These caves exhibit a blend of architectural styles, reflecting the influence of various dynasties that ruled the area during different periods.
Notably, the Gupta and Paramara dynasties left a lasting impact on the caves’ design and construction.
Historical inscriptions found in the Mandsaur Caves have been instrumental in deciphering ancient Malwa’s history and political landscape.
They provide valuable information about the rulers and dynasties that governed the region during different periods.
Conclusion
Our time traveler’s delight in Madhya Pradesh leaves us in awe of the rich tapestry of history and culture that these ancient caves have revealed to us.
Each rock-cut chamber is a silent witness to the ingenuity and devotion of the civilizations that once thrived in this region.
From the artistic brilliance of the Gupta period to the spiritual sanctuaries of the Buddhist monks, these caves have preserved the essence of India’s diverse heritage.
As we depart from this captivating journey, let us carry with us the stories of the past, cherishing the knowledge that we have stepped into the footsteps of those who walked these caves centuries ago.
May these ancient wonders continue to inspire generations, reminding us of the importance of preserving our cultural legacy for the future.
So, until we meet again on our next time-travelling expedition, may the spirit of adventure and discovery never cease to guide us in unravelling the mysteries of our remarkable world, and have a happy time travelling!