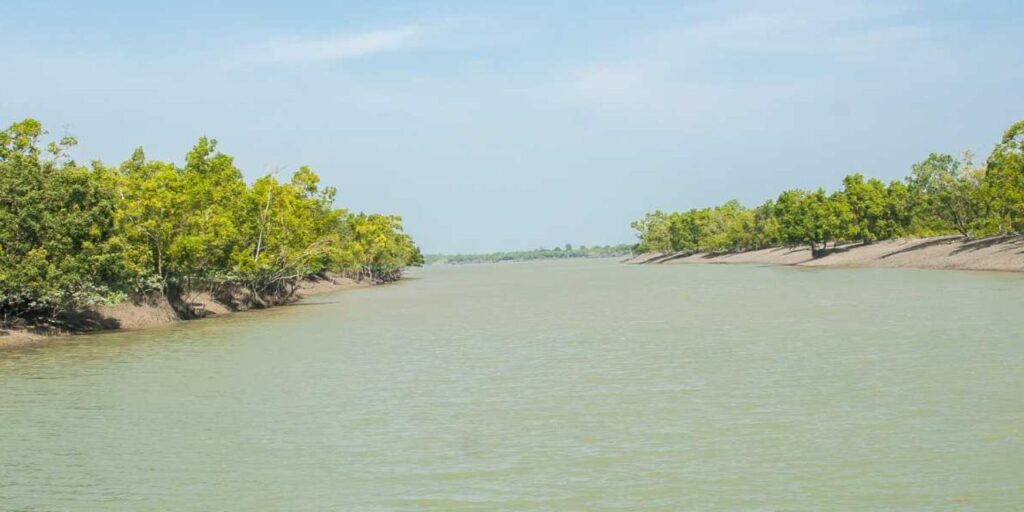
Welcome to the mystical realm of Sundarbans National Park, a sanctuary of unparalleled natural beauty nestled in the heart of the India.
The Park, a UNESCO Heritage Site, is a haven for biodiversity enthusiasts and nature lovers. The location is where the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Meghna rivers meet and form a delta.
This enchanting mangrove forest spans India and Bangladesh, creating one of the largest such reserves in the world.
“Sundarbans” means “beautiful forest,” and rightfully so. Its mesmerizing landscape, characterized by intricate waterways, dense mangrove forests, and vibrant wildlife, casts a spellbinding allure on all who venture into its depths.
The Park is renowned for its iconic Bengal tigers, which roam freely amidst the mangroves, making it one of the few places on Earth where these majestic creatures thrive in their natural habitat.
However, the allure of Sundarbans extends far beyond its famed tigers.
Its rich ecosystem supports many other wildlife, including spotted deer, crocodiles, and numerous bird species, making it a paradise for enthusiasts and photographers.
Moreover, the Park is crucial in maintaining ecological balance as a natural barrier against cyclones and tidal surges.
Whether you seek adventure, tranquillity, or a deeper connection with nature, Park offers an unforgettable experience that is as enriching as captivating.
Come, immerse yourself in the timeless charm of this extraordinary wilderness, and discover the untamed beauty of National Park.
1. Geographical Overview of Sundarbans Delta
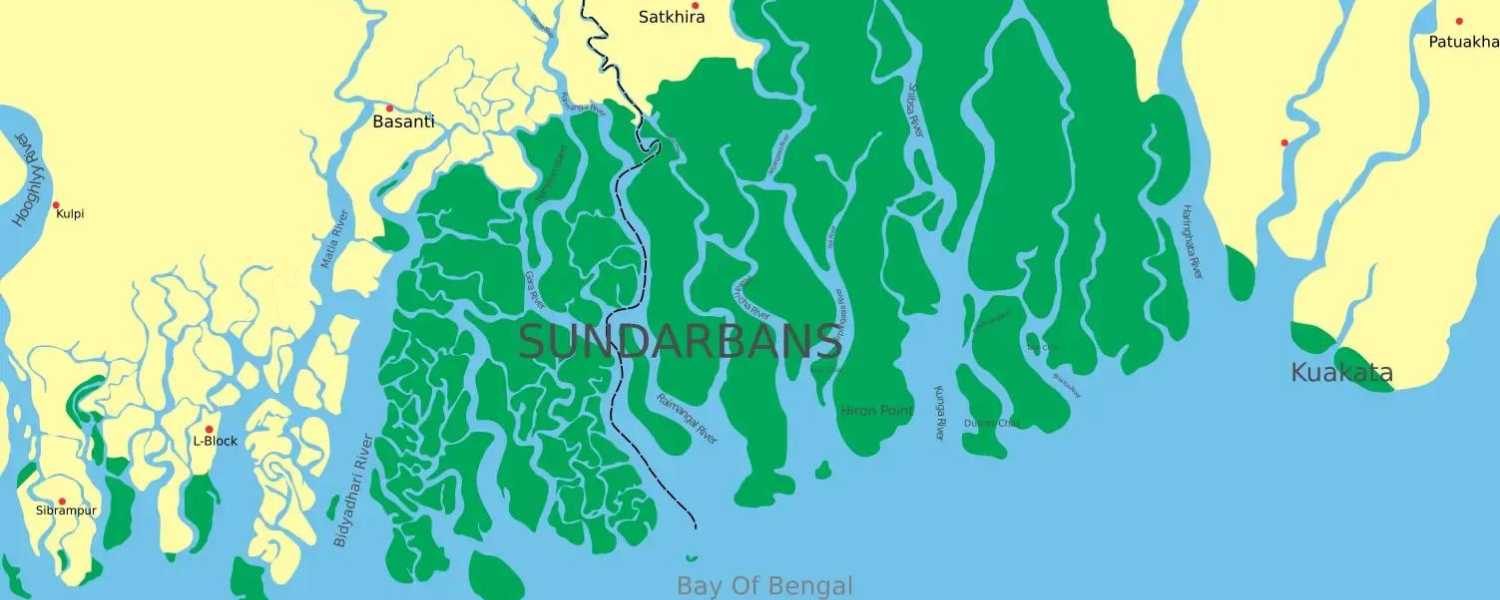
Sundarbans National Park is a UNESCO Heritage Site, nestled in India and Bangladesh’s delta region of the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Meghna rivers.
It spans over 10,000 square kilometers, making it one of the most extensive mangrove forests globally. The delta is characterized by its intricate network of waterways, mudflats, and islands shaped by tidal forces.
Its unique geography supports a rich biodiversity, making it a vital ecosystem for numerous species of flora and fauna.
2. Importance of Sundarbans in India’s Biodiversity
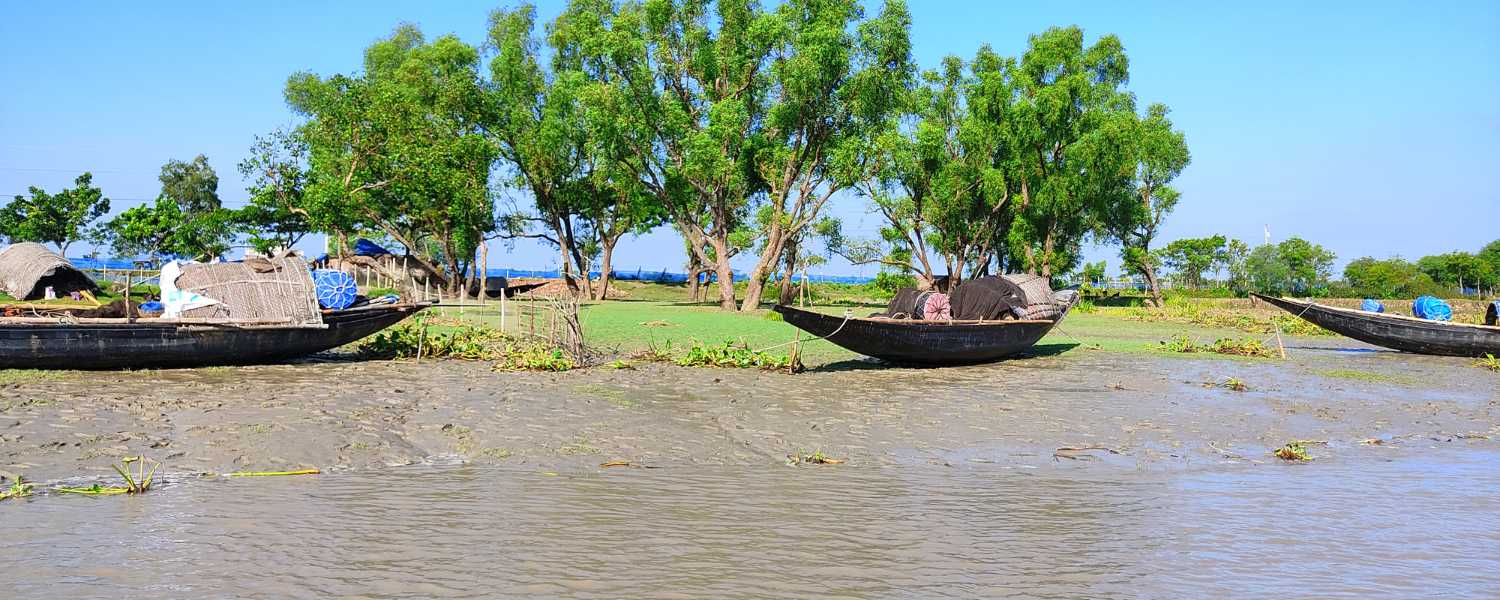

Sundarbans play a crucial role in India’s biodiversity. Its mangrove forests act as a natural barrier, protecting coastal sides from erosion and storm surges.
Additionally, it serves as a habitat for various endangered species, including the iconic Royal Bengal Tigers. The delta’s rich biodiversity contributes to the region’s ecological balance, providing livelihoods to local communities through fishing, honey collection, and tourism.
3. Flora and Fauna Diversity in Sundarbans

The Sundarbans are home to a diverse range of flora and fauna. Mangrove species such as Sundari, Gewa, and Goran dominate the landscape and adapt to thrive in saline and waterlogged conditions.
The region supports many wildlife, including spotted deer, wild boar, and rhesus macaques. Its waterways are inhabited by crocodiles, river dolphins, and various fish species, making it a hotspot for biodiversity enthusiasts and researchers.
4. The Royal Bengal Tigers of Sundarbans
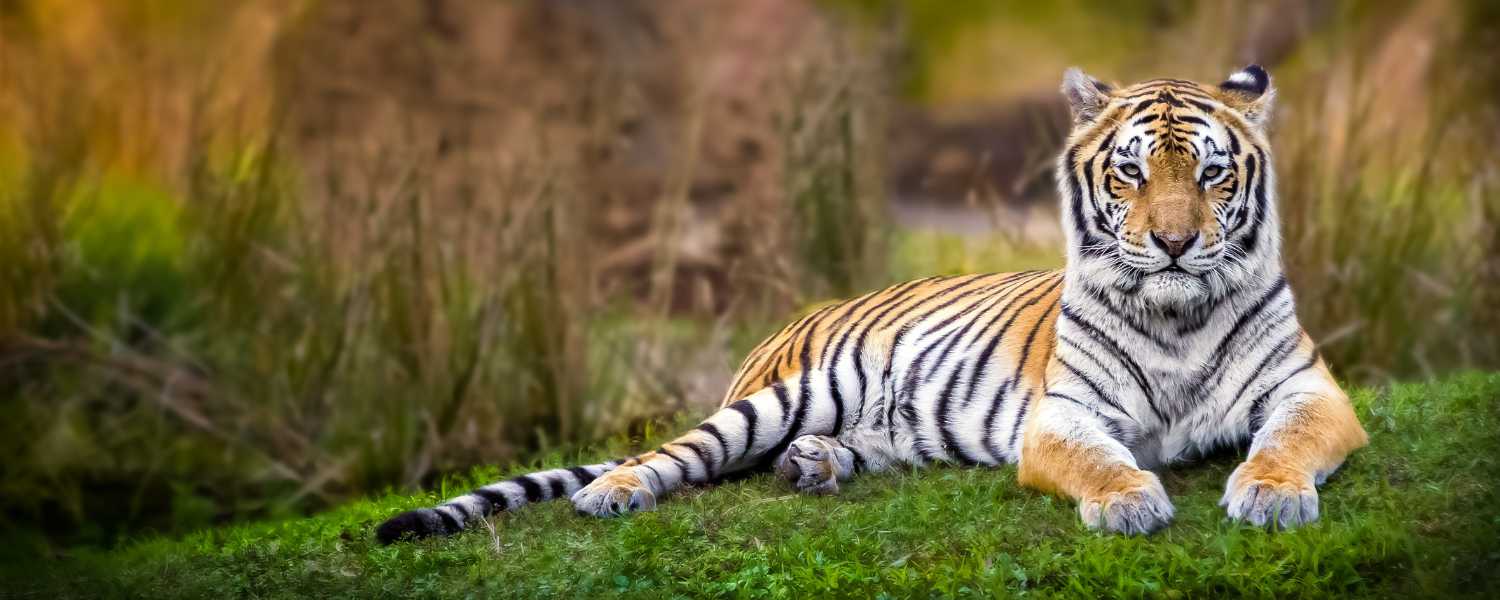

One of the most iconic inhabitants of Sundarbans is the Royal Bengal Tiger. Known for its adaptation to the mangrove environment, these tigers are excellent swimmers and are skilled at hunting in water.
However, their population faces threats from habitat loss, human-wildlife conflict, and climate change. Efforts to conserve these magnificent animals and their natural habitat are being implemented, ensuring their survival for future generations.
5. Mangrove Ecosystem: A Closer Look
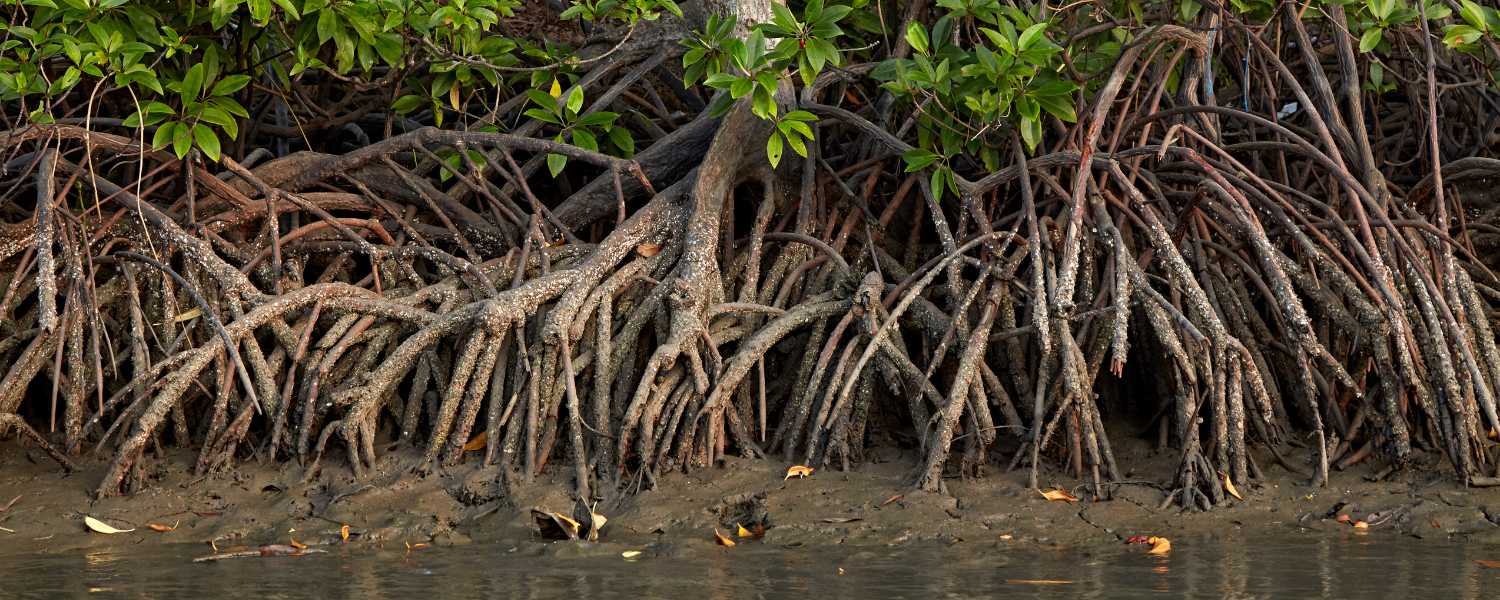

The mangrove ecosystem of Sundarbans is a marvel of nature. Mangroves play a vital role in carbon sequestration, helping mitigate climate change. Their intricate root systems provide habitats for various marine species and act as nurseries for fish and crustaceans.
Moreover, mangroves are a natural buffer against coastal erosion and storms, safeguarding coastal communities and infrastructure. Understanding and preserving this delicate ecosystem is essential for wildlife and humans’ well-being.
6. A Haven for Bird Watching
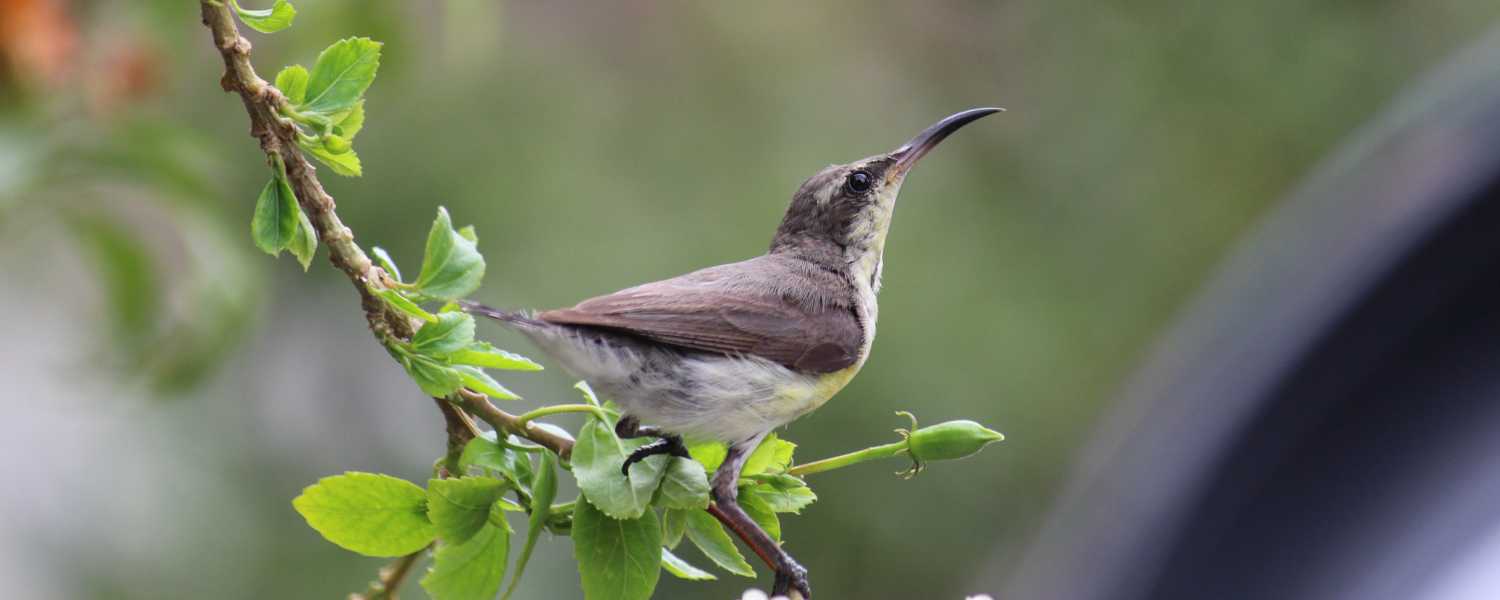

Sundarbans National Park is a paradise for bird enthusiasts, offering a diverse range of avian wonders amidst its breathtaking natural beauty.
Bird watching in Sundarbans is an awe-inspiring experience, with the chance to spot rare and exotic species against the backdrop of lush mangrove forests and winding waterways.
The Park is teeming with life, from majestic raptors like the White-bellied Sea Eagle to vibrant kingmakers and elusive owls.
Guided tours allow visitors to learn about these fascinating creatures’ unique behaviors and habitats, making for an unforgettable adventure in nature’s aviary.
7. Sundarbans’ Vital Role in Climate Change Mitigation
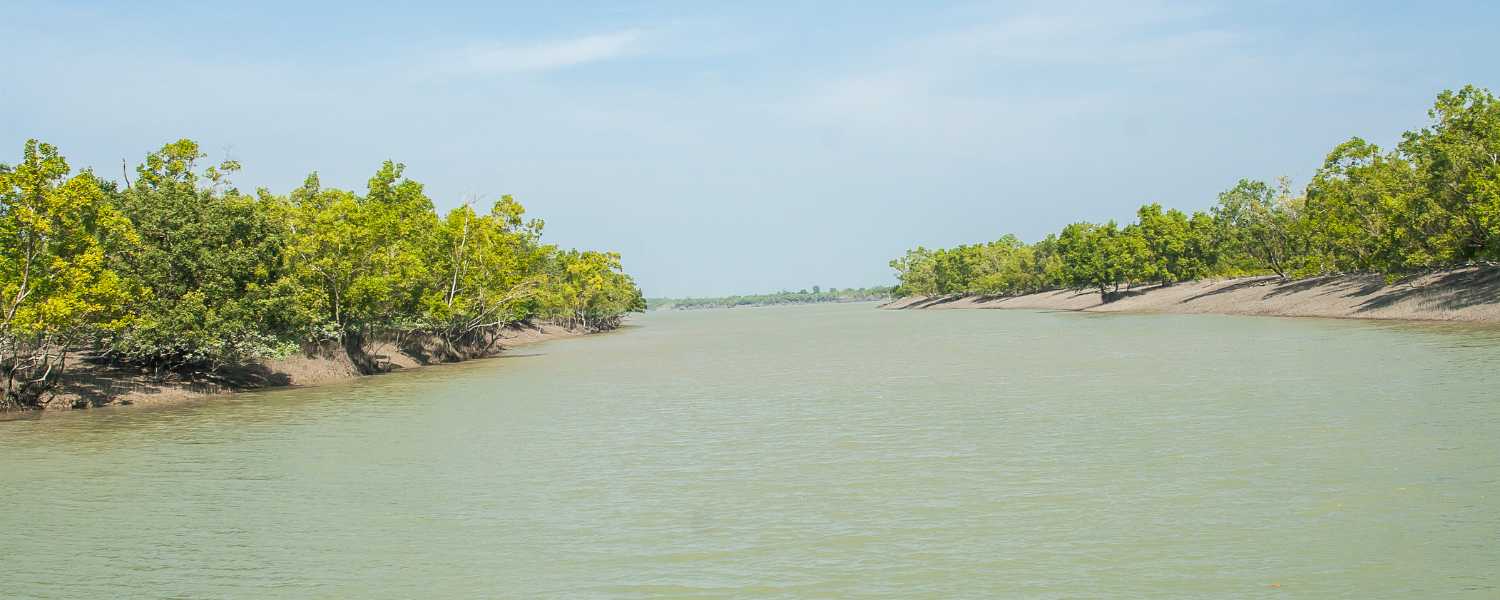

The National Park is crucial in mitigating climate change by serving as a carbon sink. The dense mangrove forests of the Sundarbans absorb Large quantities of carbon dioxide that need to be removed from the atmosphere, helping to reduce greenhouse gas levels and combat global warming.
Additionally, these mangroves act as a protective barrier against coastal erosion and storm surges, safeguarding nearby communities and biodiversity by preserving and restoring the Sundarbans ecosystem.
8. Conservation Initiatives
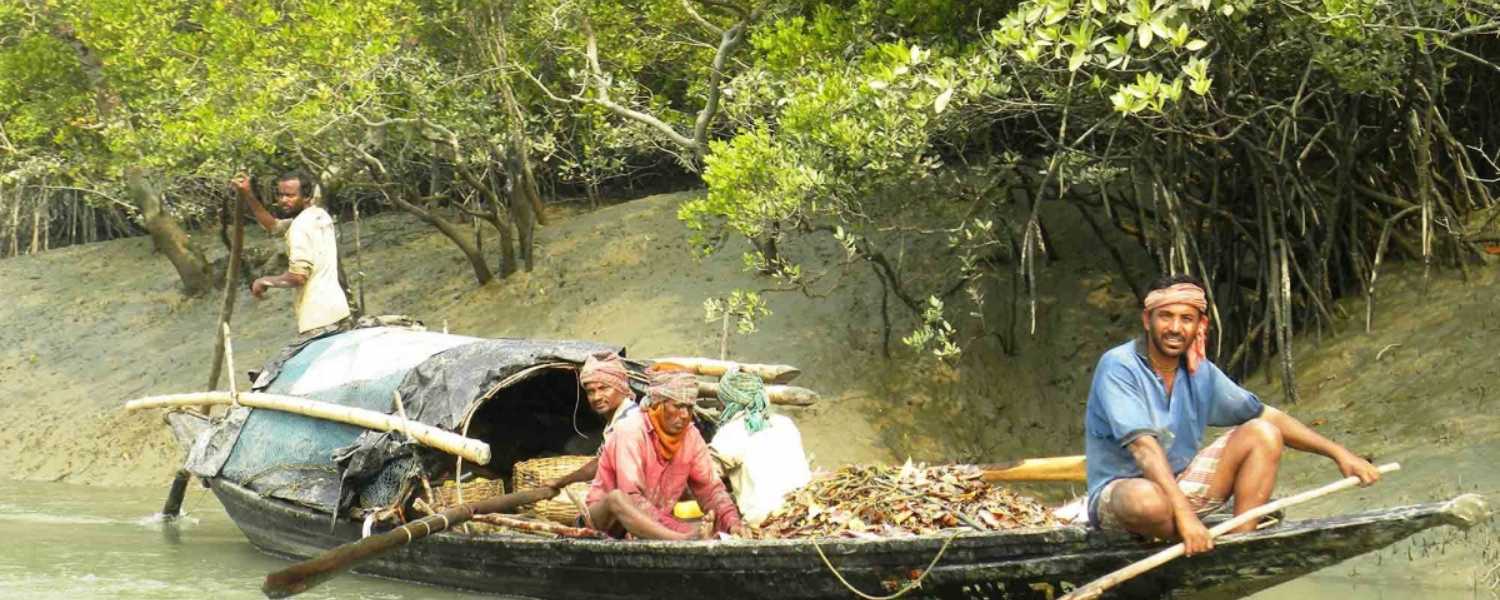

Efforts to conserve the Sundarbans National Park are underway to safeguard its unique biodiversity and ecological integrity.
Both conservation organizations and government agencies are working to address threats like habitat loss, poaching, and pollution.
Initiatives include habitat restoration projects, community-based conservation programs, and enhanced law enforcement measures.
Promoting sustainable livelihoods and awareness about the importance of biodiversity conservation aims to protect the Sundarbans’ heritage for future generations to enjoy.
9. Sundarbans: A UNESCO World Heritage Site
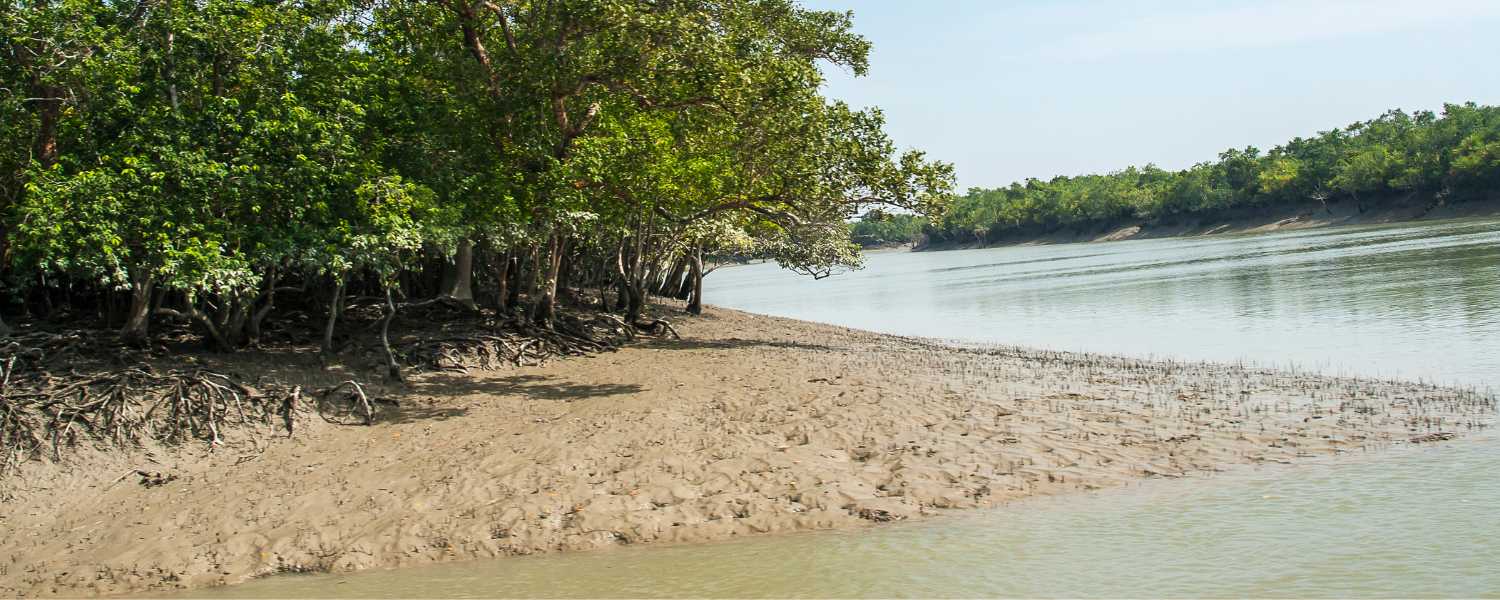

The National Park is recognized as a UNESCO Heritage Site, celebrating its outstanding universal value and significance for humanity.
As one of the largest mangrove ecosystems in the world, the Sundarbans is home to an array of plant/animal species, including the iconic Royal Bengal Tiger.
Its ecology and cultural heritage make it a globally significant biodiversity conservation and scientific research site. UNESCO designation highlights the need for international cooperation and collective action to preserve and sustainably manage this precious natural treasure for the benefit of present and future generations.
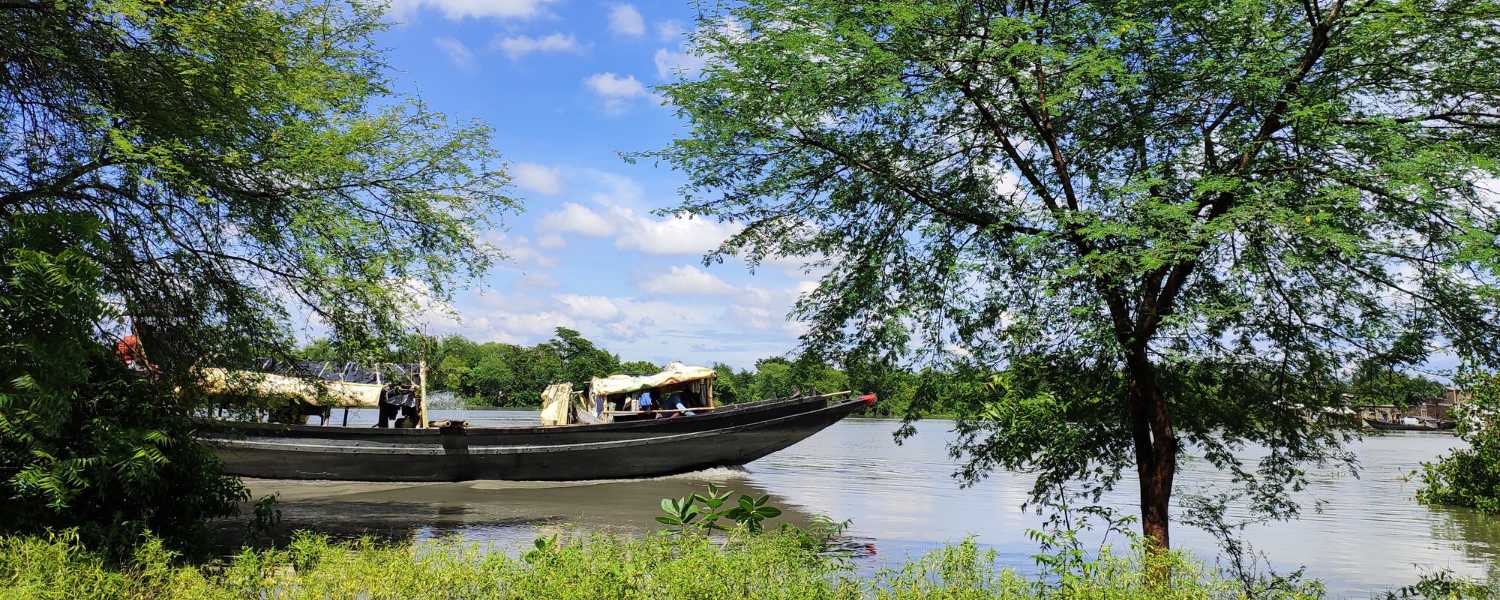
10. Exploring Sundarbans National Park by Boat
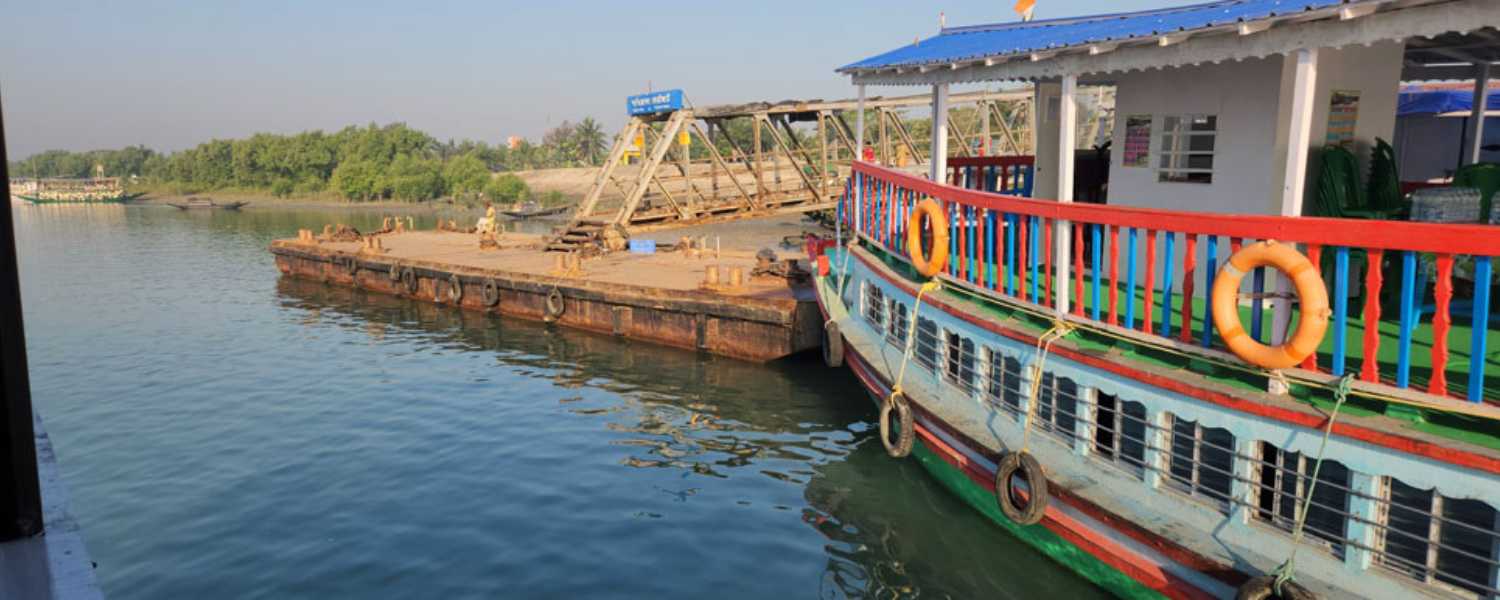

Embark on an unforgettable journey through the captivating landscapes of a national park in India. Explore its unparalleled beauty and rich biodiversity from the comfort of a boat.
This immersive experience offers a unique perspective, allowing you to marvel at the wonders of nature while cruising through serene waters.
Guided boat tours take visitors through winding waterways, dense mangrove forests, and tranquil creeks, providing opportunities to spot wildlife up close in their natural habitat.
From the iconic Bengal Tiger to playful dolphins and colorful birds, every turn reveals new wonders waiting to be discovered.
Experienced guides share their knowledge of the Park’s sociology and cultural heritage, enriching the journey with insights and stories that bring the Sundarbans to life.
Whether cruising at dawn or dusk, a boat excursion in the Sundarbans promises an unforgettable adventure amidst nature’s splendor.
11. Local Communities and Their Relationship with Sundarbans
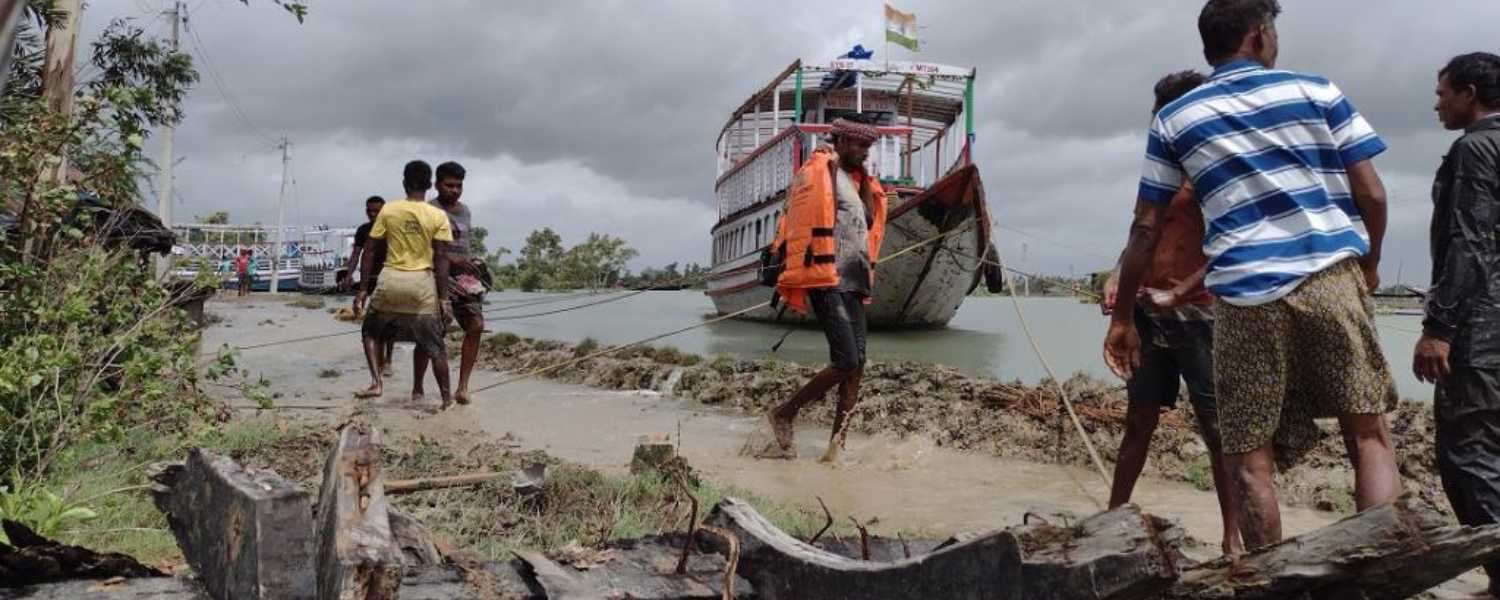

The National Park is intricately linked with the lives of local communities residing in its vicinity. These communities depend on the Park’s resources, including fishing and collecting forest products like honey and wood. Their cultural practices and traditions are deeply rooted in the natural rhythms of the Sundarbans.
12. Threats to the Ecosystem: Human and Natural Challenges
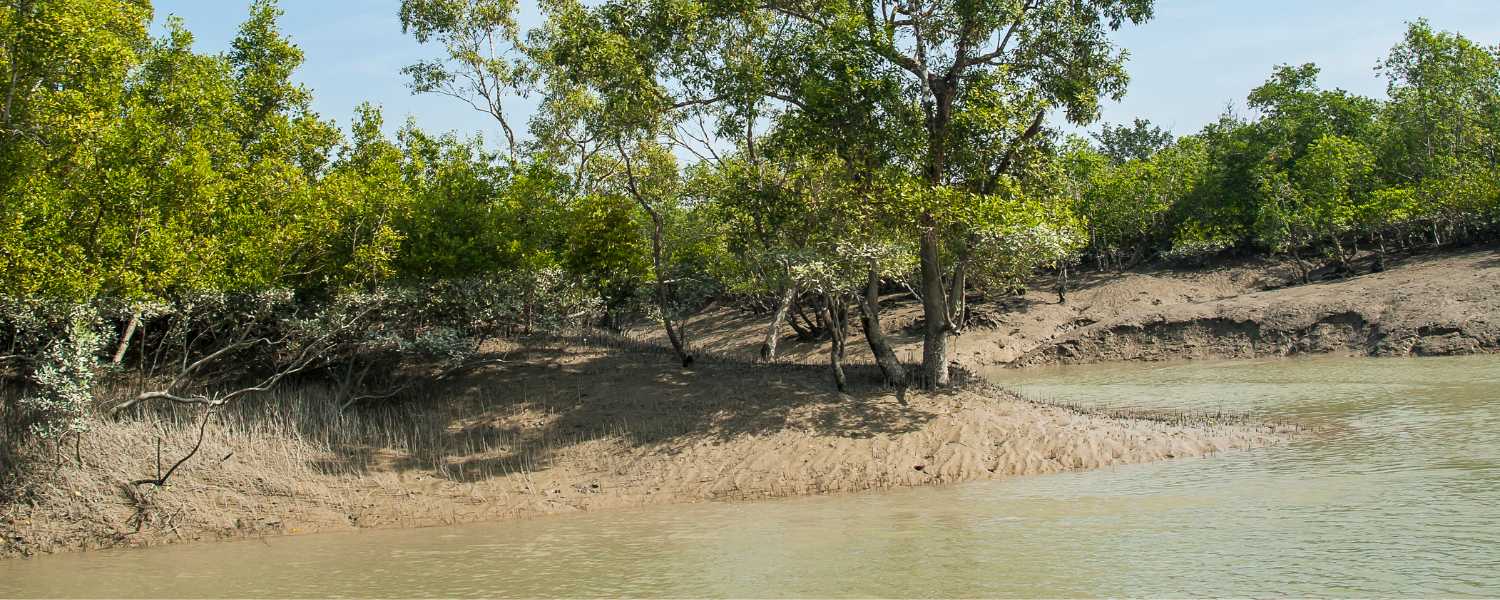

The Sundarbans face various threats, both human-induced and natural. Human activities such as deforestation, pollution, and illegal poaching pose significant risks to the delicate ecosystem.
Additionally, natural challenges like cyclones and rising sea levels further exacerbate the vulnerability of this UNESCO World Heritage Site.
13. Unique Features of Sundarbans’ Flora
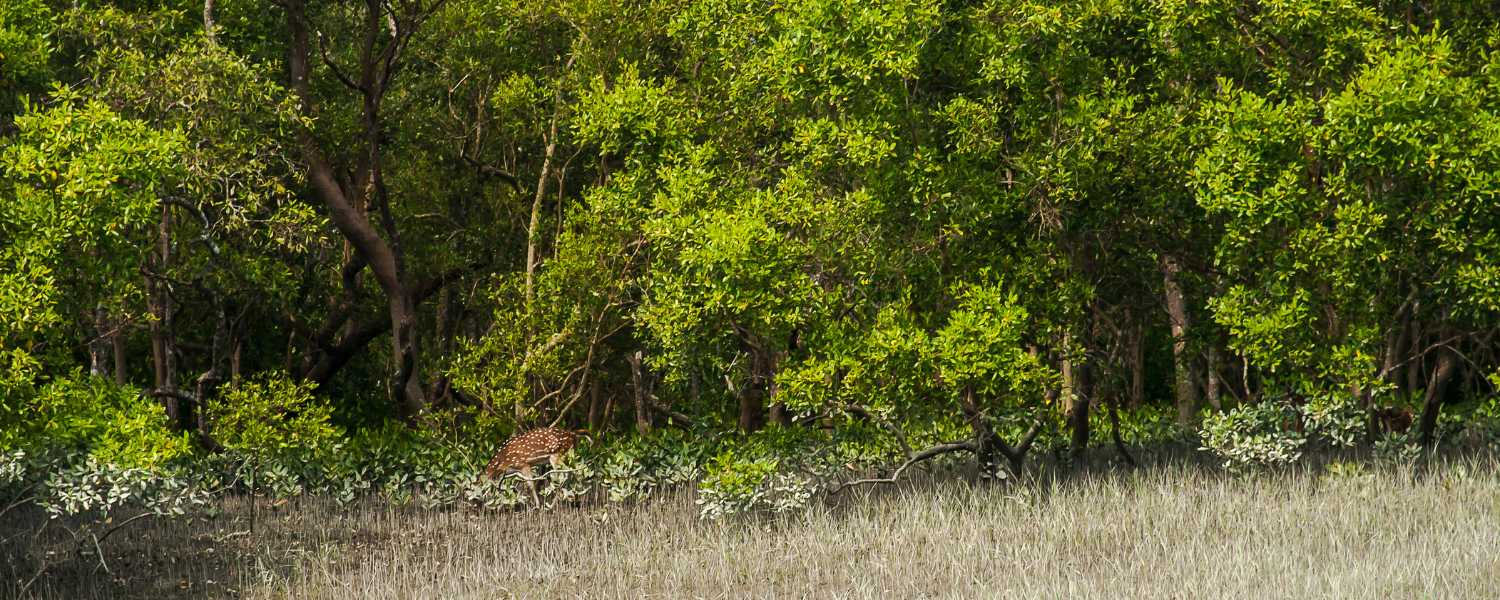

One of the most striking features of the Sundarbans is its unique mangrove forests. These dense forests are home to diverse flora, including the iconic Sundari trees, after which the region is named.
Adapted to saline conditions, these mangroves play a crucial role in stabilizing coastal areas and providing habitat for numerous species of plants/animals.
14. Sundarbans in Literature and Folklore

The Sundarbans hold a special place in literature and folklore, inspiring countless tales and legends. From the mythical stories of Bonbibi, the forest goddess, to the works of renowned authors like Amitav Ghosh, the Sundarbans have captured the imagination of writers and storytellers for centuries.
15. Ecotourism Initiatives in Sundarbans
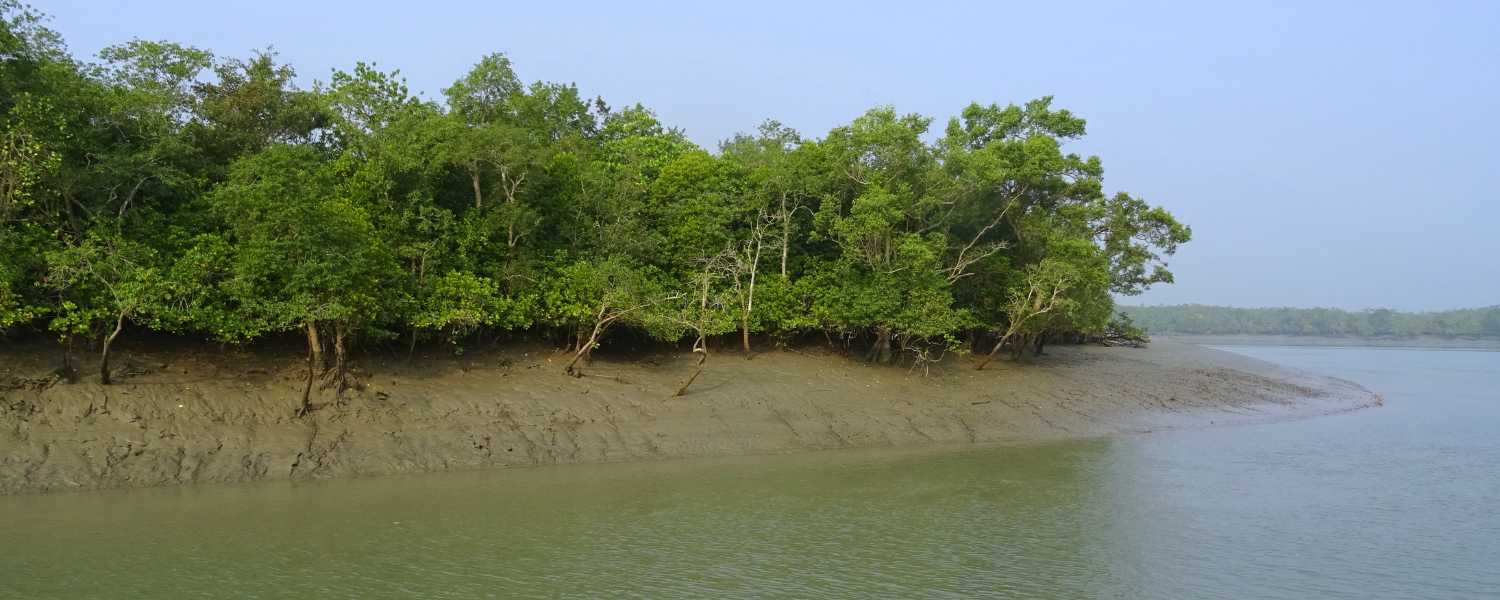

Recognizing the importance of sustainable tourism, various ecotourism initiatives have been launched in the National Park.
These initiatives promote responsible travel practices, allowing visitors to experience the Park’s natural beauty and learn about its conservation efforts.
Through eco-friendly tourism, efforts are made to mitigate the impact of human activities on the Sundarbans’ fragile ecosystem.
16. A Monsoon Photographer’s Paradise
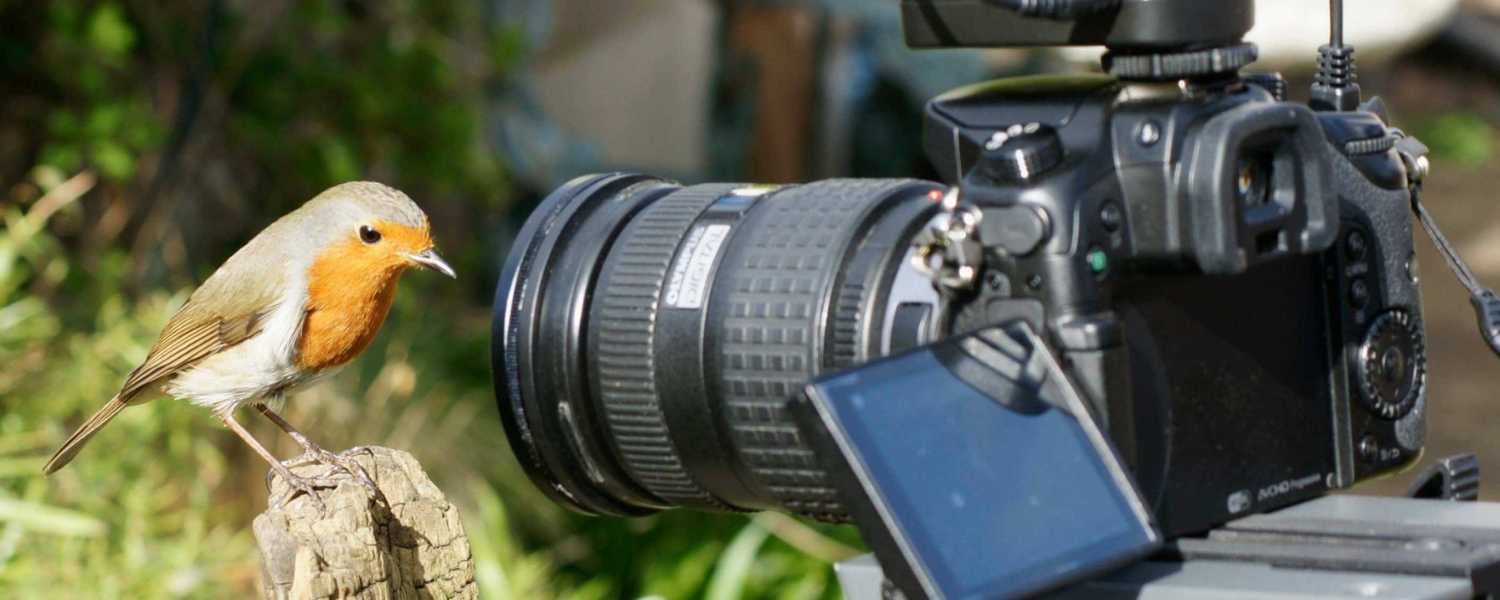

During the monsoon season, the Sundarbans National Park transforms into a mesmerizing landscape, attracting photographers from around the globe.
This UNESCO Heritage Site, nestled in the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Meghna rivers delta, offers a unique spectacle of lush greenery, misty mornings, and dramatic skies.
The interplay of light and shadow creates a magical ambiance, perfect for capturing stunning mangrove forests and diverse wildlife shots.
17. Rare and Endangered Species in Sundarbans
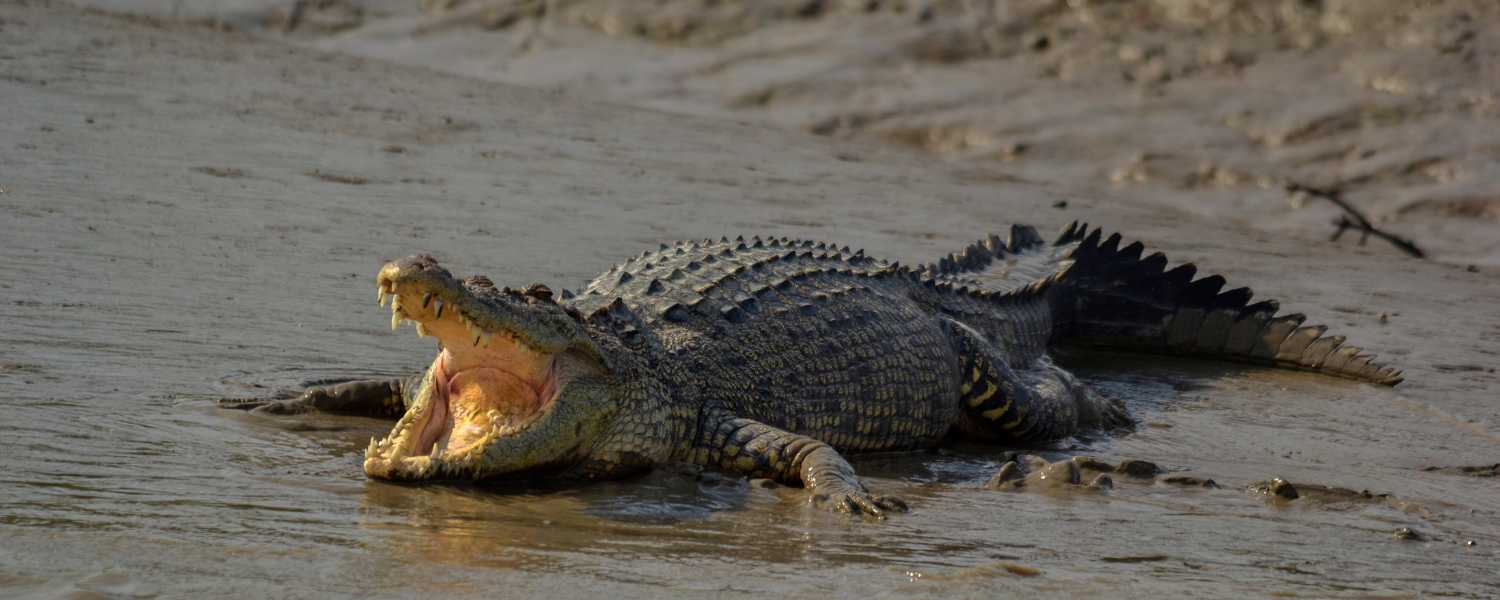

The Sundarbans are renowned for their rich biodiversity, harboring several rare and endangered species. Among them are the majestic Royal Bengal Tiger, elusive Irrawaddy dolphins, and the endangered Gangetic river dolphin.
These species rely on the mangrove ecosystem for their survival, making the Sundarbans a vital sanctuary for their conservation.
18. Sundarbans’ Contribution to Fisheries
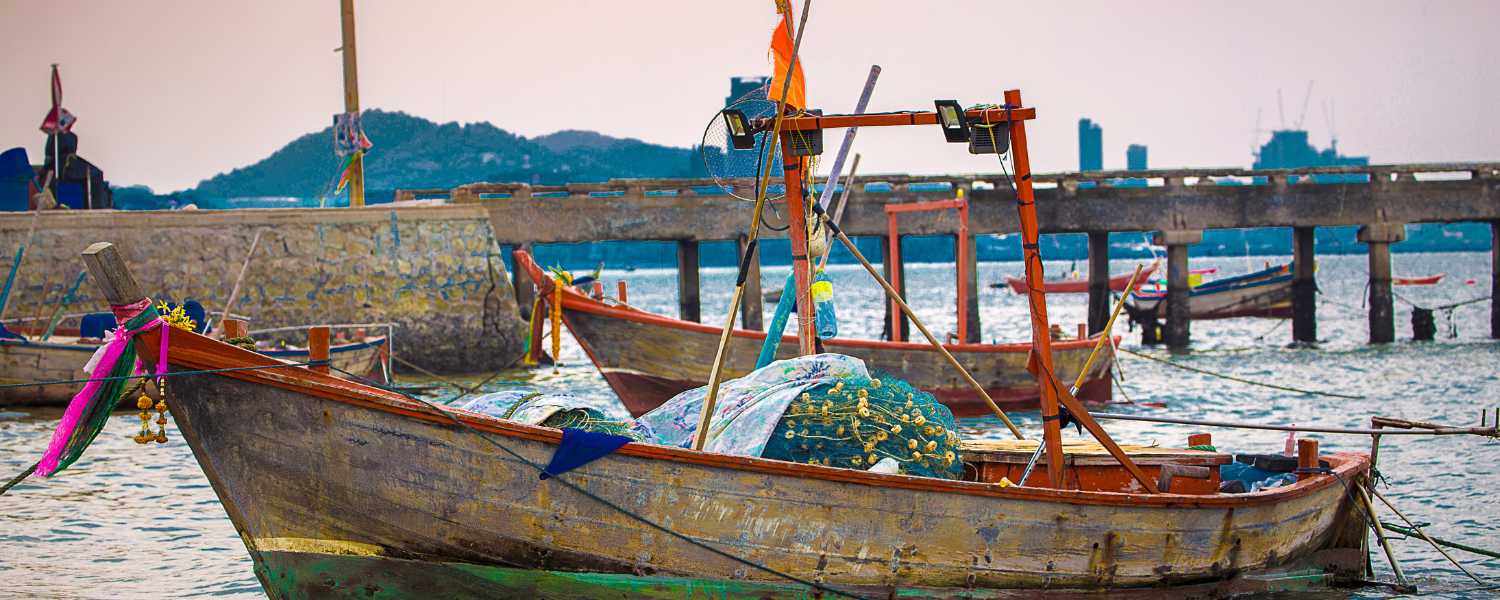

The Sundarbans serve as a haven for wildlife and play a crucial role in sustaining local livelihoods through fisheries. The intricate network of waterways and mangrove forests provides a fertile breeding ground for various fish species, supporting the livelihoods of thousands of coastal communities.
19. Sundarbans in the Eyes of Researchers and Scientists
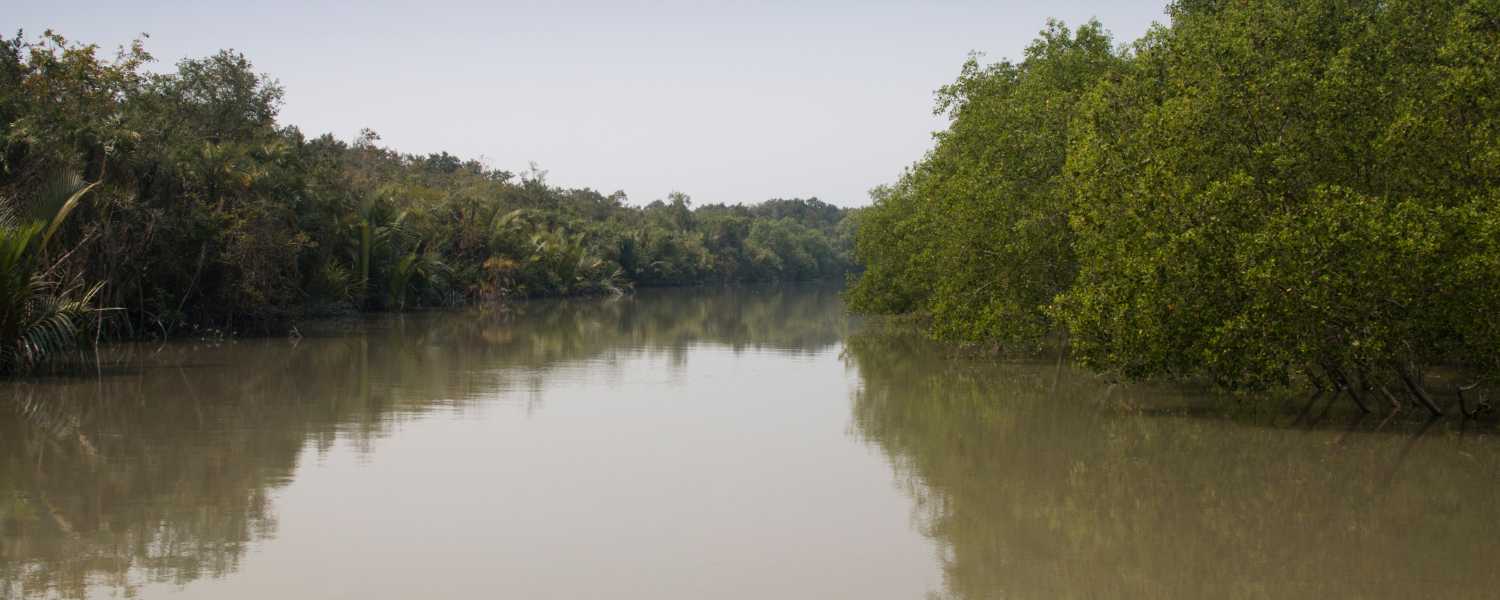

Researchers and scientists are increasingly drawn to the Sundarbans to study its unique ecology and the impacts of climate change.
With sea levels and changing nature patterns, the Sundarbans face numerous challenges, including habitat loss and saltwater intrusion.
Understanding these dynamics is essential for devising effective conservation strategies to safeguard this invaluable ecosystem for future generations.
20. A Haven for Biodiversity Researchers
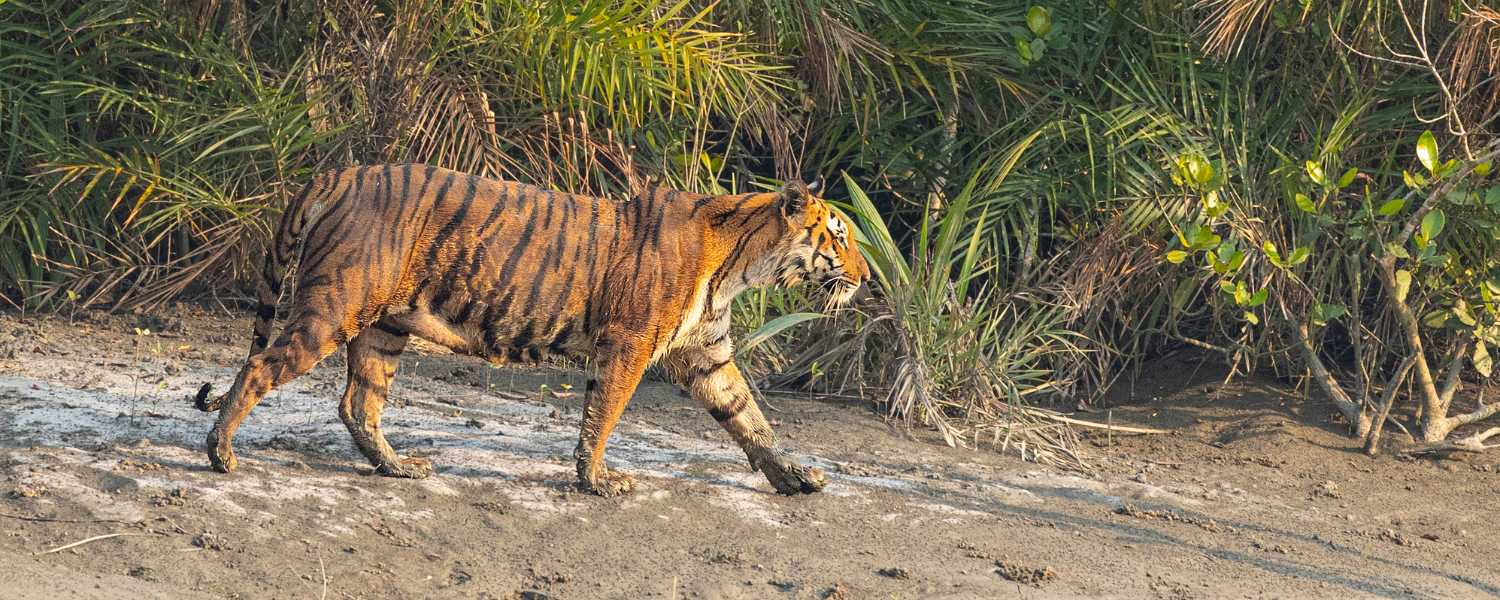

Nestled in the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Meghna rivers delta, the National Park is a treasure trove for biodiversity enthusiasts and researchers alike.
Its dense mangrove forests, winding waterways, and diverse habitats harbor unique flora and fauna, making it a prime destination for scientific exploration.
Researchers flock to this UNESCO World Heritage Site to study its rich ecosystems, from the elusive Royal Bengal Tigers to the myriad bird species and marine life that call it home.
21. Challenges Faced by Conservationists in Sundarbans
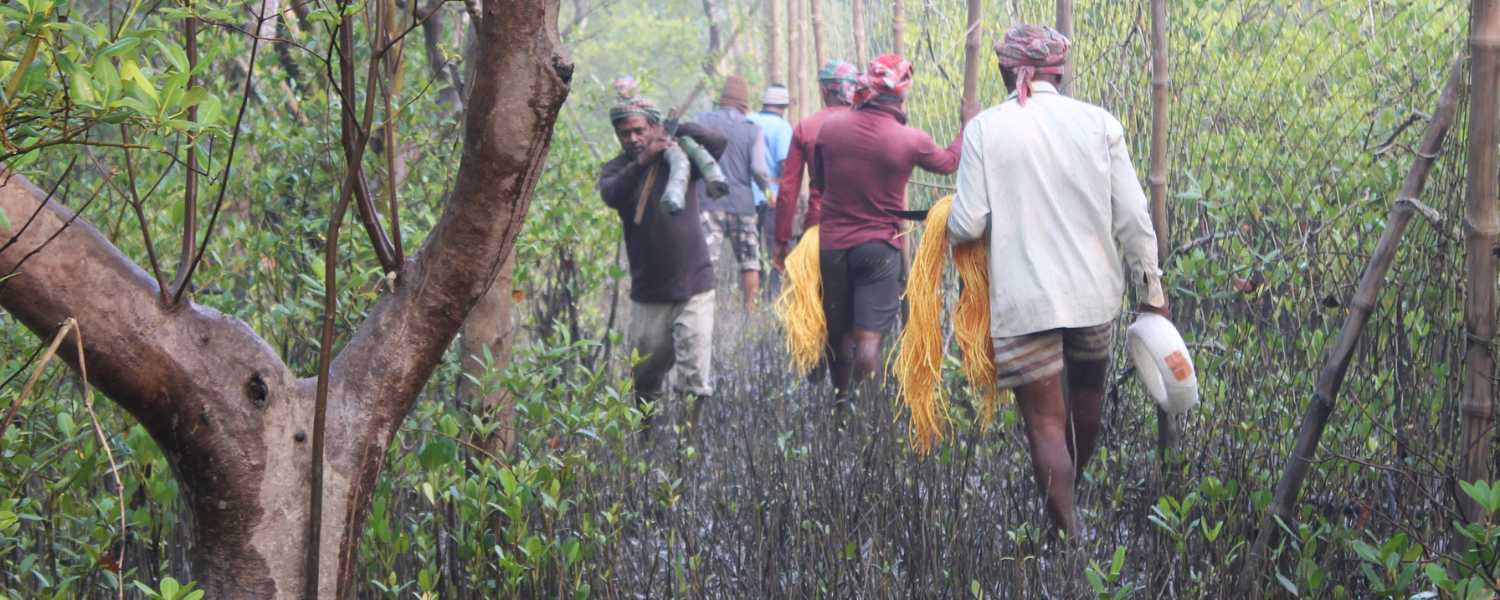

However, amidst its ecological marvels, it faces formidable challenges that test the resolve of conservationists. Rampant poaching, habitat degradation, and human-wildlife conflict pose significant threats to the balance of this pristine ecosystem.
Conservation efforts must navigate through bureaucratic hurdles, resource limitations, and the complexities of socio-economic dynamics to safeguard the Park’s biodiversity for future generations.
22. Sundarbans’ Impact on Surrounding Ecosystems
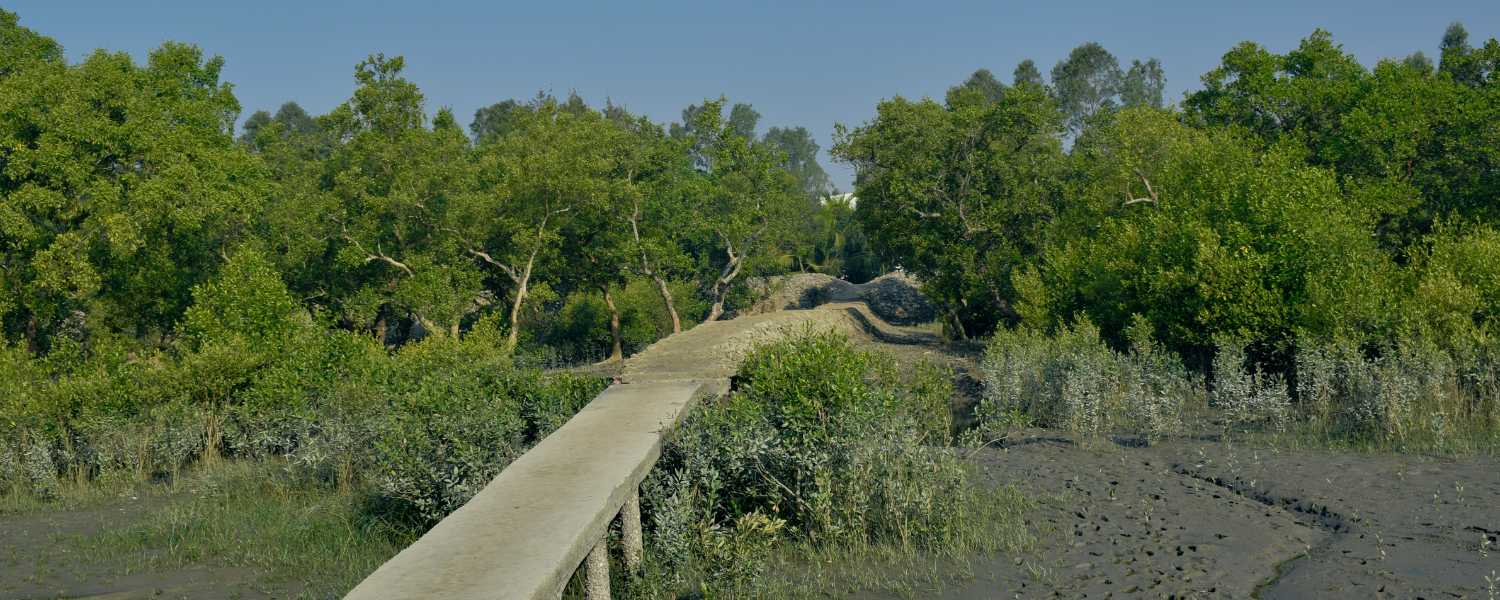

Beyond its borders, the influence of PParkext extends far and wide, profoundly shaping the surrounding ecosystems. The intricate network of mangroves acts as a natural barrier, shielding coastal communities from the wrath of cyclones and tidal surges.
Its rich sediment deposits nourish adjacent agricultural lands and support thriving fisheries, underscoring its vital role in sustaining nature and human livelihoods.
23. Sundarbans and the Cultural Heritage of the Region
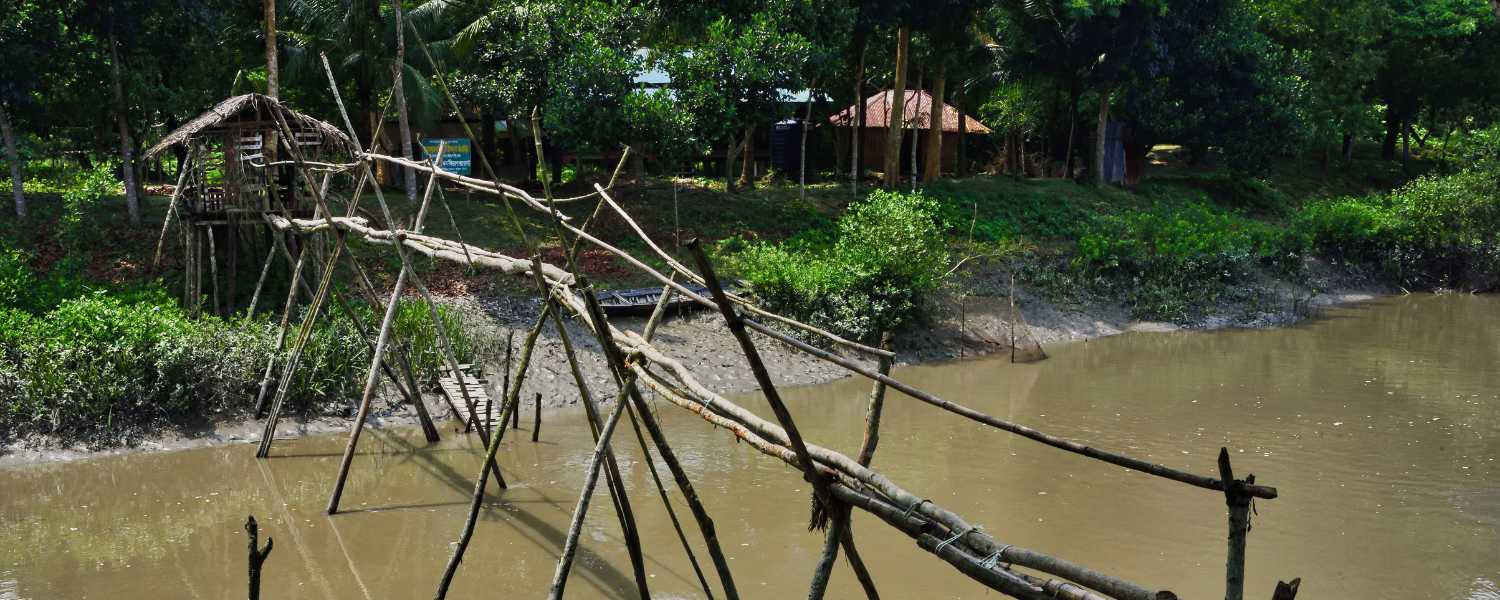

Moreover, PPark is not merely a wildlife sanctuary but deeply intertwined with the region’s cultural heritage. Indigenous communities, such as the Sundarbans’ Munda and Bawaliya tribes, have forged symbiotic relationships with the mangrove forests for generations, relying on its resources for sustenance and spiritual fulfillment.
Their folklore, rituals, and traditional knowledge underscore the intrinsic link between humans and nature, enriching the tapestry of cultural diversity in the Sundarbans region.
24. Sustainable Tourism Practices in Sundarbans National Park
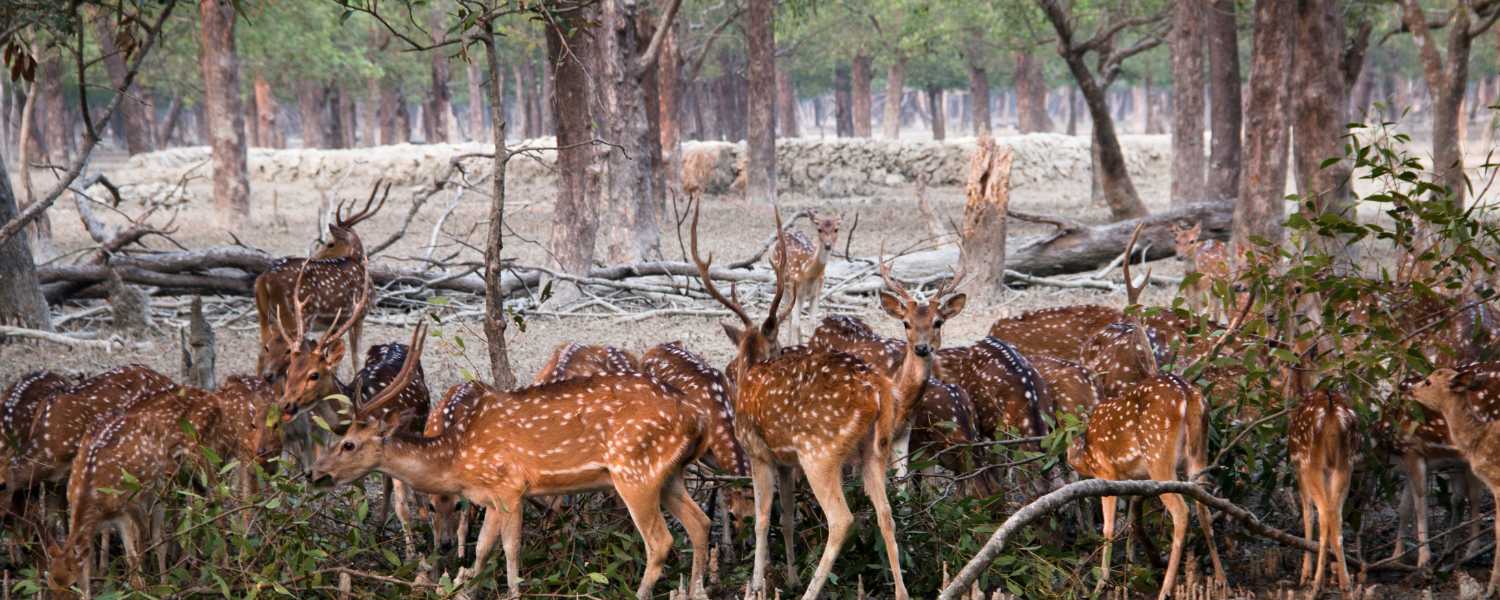

It is a UNESCO World Heritage renowned for its rich biodiversity and unique ecosystem. Sustainable tourism practices are essential to preserve this delicate environment.
These aim to minimize the negative impacts of tourism on the Sundarbans while maximizing the benefits to local communities and wildlife.
Measures such as controlled visitor numbers, eco-friendly accommodations, and responsible waste management help ensure the Park’s long-term viability.
25. The Future of Sundarbans National Park: Conservation Goals

Sundarbans National Park’s conservation efforts focus on protecting its diverse flora and fauna. Key goals include habitat restoration, anti-poaching initiatives, and community engagement programs.
By involving local communities in conservation efforts, stakeholders can collaborate to safeguard the Park’s natural resources for future generations.
26. Personal Experiences and Travel Tips for Sundarbans
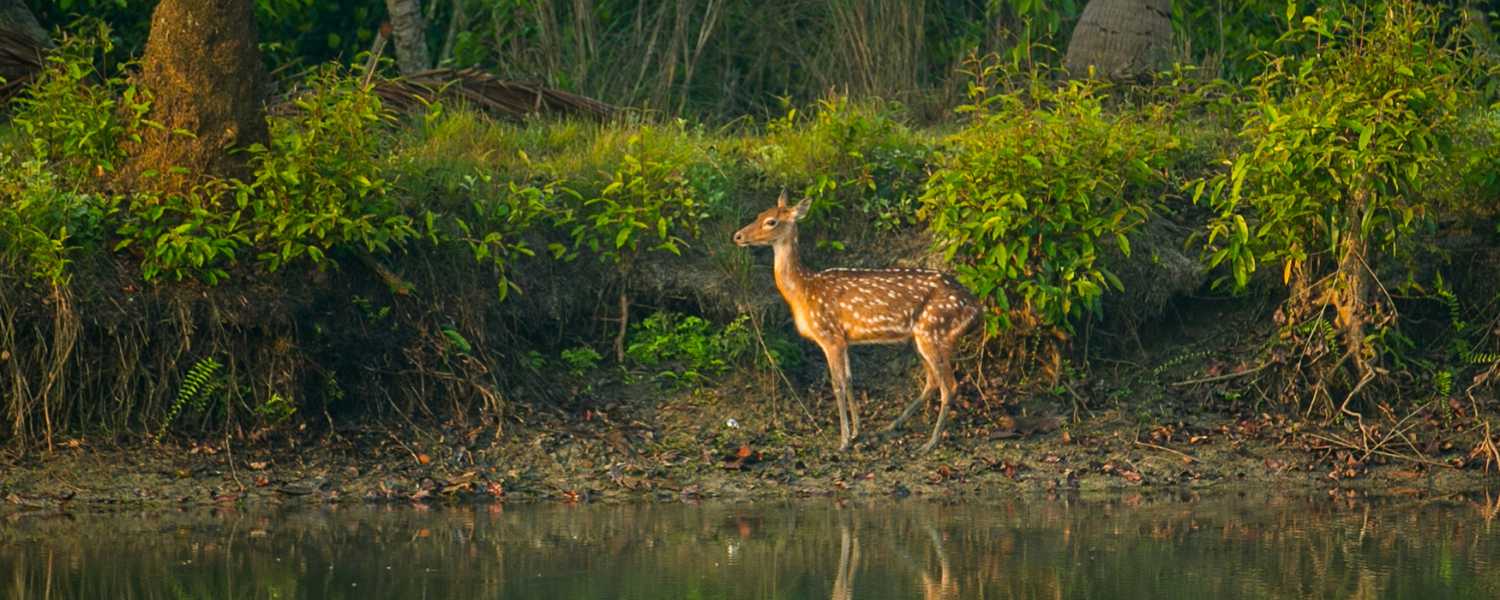

Exploring Sundarbans Park offers travelers a chance to connect with nature remarkably.
From thrilling boat safaris to tranquil nature walks, there’s something for everyone to enjoy.
To make the most of your visit, pack appropriate clothing, insect repellent, and binoculars for wildlife spotting.
Additionally, hiring local guides not only enhances the experience but also supports the livelihoods of residents.
Respect nature and follow park rules to ensure a memorable and responsible journey.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Sundarbans National Park is a beacon of biodiversity and natural wonder. Its unique mangrove ecosystem, sprawling across India and Bangladesh, shelters many species, some of which are rare and endangered.
The Park is a habitat for iconic Bengal tigers and provides refuge to numerous other animals, birds, and marine life. Its importance extends beyond its rich fauna, as the mangrove forests act as a vital barrier against natural calamities, shielding the inland areas from the wrath of cyclones and tidal surges.
Visiting the National Park offers an unparalleled opportunity to witness nature’s resilience and beauty firsthand. The tranquil boat rides through winding creeks allow visitors to immerse themselves in the serene surroundings, where every turn reveals a new spectacle of wildlife and lush greenery.
Moreover, the parkserves act as a living laboratory for researchers and conservationists, offering invaluable insights into the balance of ecosystems and the need for their preservation.The PParkis is not just a tourist destination but a sanctuary embodying the harmonious coexistence of diverse life forms.
Preserving this natural treasure is not only a moral imperative but also crucial for ensuring future generations’ well-being and maintaining our planet’s ecological balance. As stewards of this invaluable heritage, our collective responsibility is safeguarding the PPark for future generations.
FAQ
What is Sundarbans National Park?
Sundarbans National Park is a UNESCO World Heritage Site located in India and Bangladesh’s delta region of the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Meghna rivers. It’s renowned for its unique mangrove forests and diverse wildlife.
Why is Sundarbans National Park famous?
This National Park is famous for being the world’s largest tidal mangrove forest and harboring the iconic Royal Bengal Tiger, along with other rare species like the estuarine crocodile and the Gangetic dolphin.
How can I reach Park?
You can access Sundarbans National Park through various entry points, mainly from cities like Kolkata in India and Khulna in Bangladesh. You can take boat rides or cruises to explore the Park from there.
What activities can I do at the Park?
Visitors can indulge in activities like wildlife safaris, birdwatching, boat cruises, and nature walks to explore the rich biodiversity of the mangrove forests. Additionally, cultural experiences such as visiting local villages and interacting with the communities are available.
Is it safe to visit the National Park?
While the Park offers thrilling experiences, tourists are requested to follow safety guidelines provided by authorities, especially during boat rides and jungle excursions. Being mindful of wildlife and following instructions from guides ensures a safe and enjoyable visit.