Welcome to the great city of Kolkata, where history and modernity converge in a mesmerizing tapestry of the architecture of India.
Nestled along the banks of the Hooghly River, Kolkata boasts a rich and diverse architecture of India that reflects its storied past and dynamic present.
The architecture of India of Kolkata is a captivating blend of colonial influences, indigenous craftsmanship, and contemporary designs.
From majestic British-era buildings adorned with intricate carvings and grand facades to charming colonial bungalows tucked away in leafy neighborhoods, each structure tells a unique story of the city’s evolution over the centuries.
One of Kolkata’s most iconic landmarks is the Victoria Memorial, a magnificent marble tower built in memory of Queen Victoria.
Its majestic dome and sprawling gardens make it a popular destination for locals and tourists. Another architectural gem is the Howrah Bridge, an engineering marvel that spans the Hooghly River and connects Kolkata with its bustling suburb of Howrah.
In addition to colonial-era buildings, Kolkata is home to stunning examples of contemporary architecture, including sleek skyscrapers, innovative cultural centers, and avant-garde residential complexes.
These modern structures starkly contrast the city’s historical landmarks, yet together, they form a captivating tapestry that reflects Kolkata’s ever-changing identity.
Join us as we embark on a journey through the architectural marvels of Kolkata, where the past meets the present in a harmonious blend of tradition and innovation.
1. Indus Valley Civilization Architecture
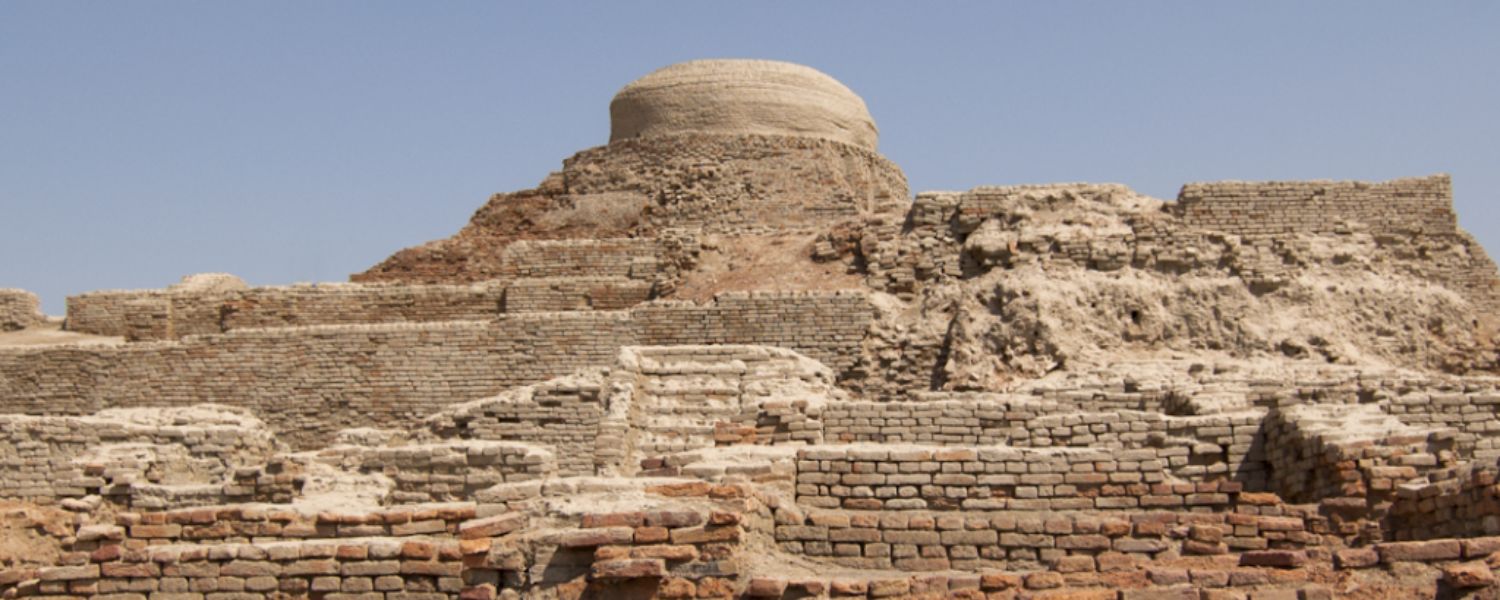

The architecture of India of the Indus Valley Civilization, one of the earliest urban societies in the world, showcases remarkable urban planning and engineering skills.
Cities like Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa had well-organized streets, drainage systems, and multi-story houses made of baked bricks.
The Great Bath in Mohenjo-Daro is a prime example, illustrating advanced water management and architectural sophistication.
2. Mauryan Architecture
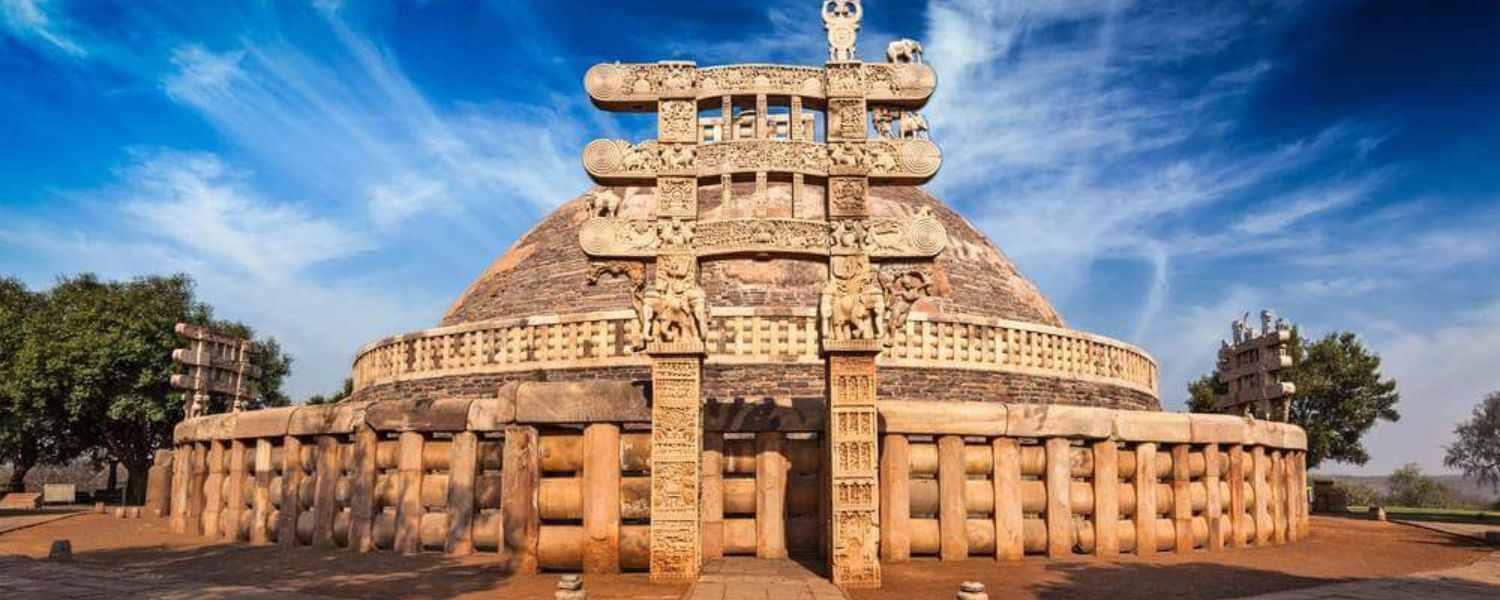

Mauryan architecture of India flourished during the Mauryan Empire in ancient India under the patronage of Emperor Ashoka.
Notable structures include the famous Ashoka Pillars, carved with edicts and topped by exquisite animal sculptures.
The Sanchi Stupa, an iconic Mauryan monument, reflects the early Buddhist architecture of India with its hemispherical dome and intricate carvings.
3. Buddhist Architecture
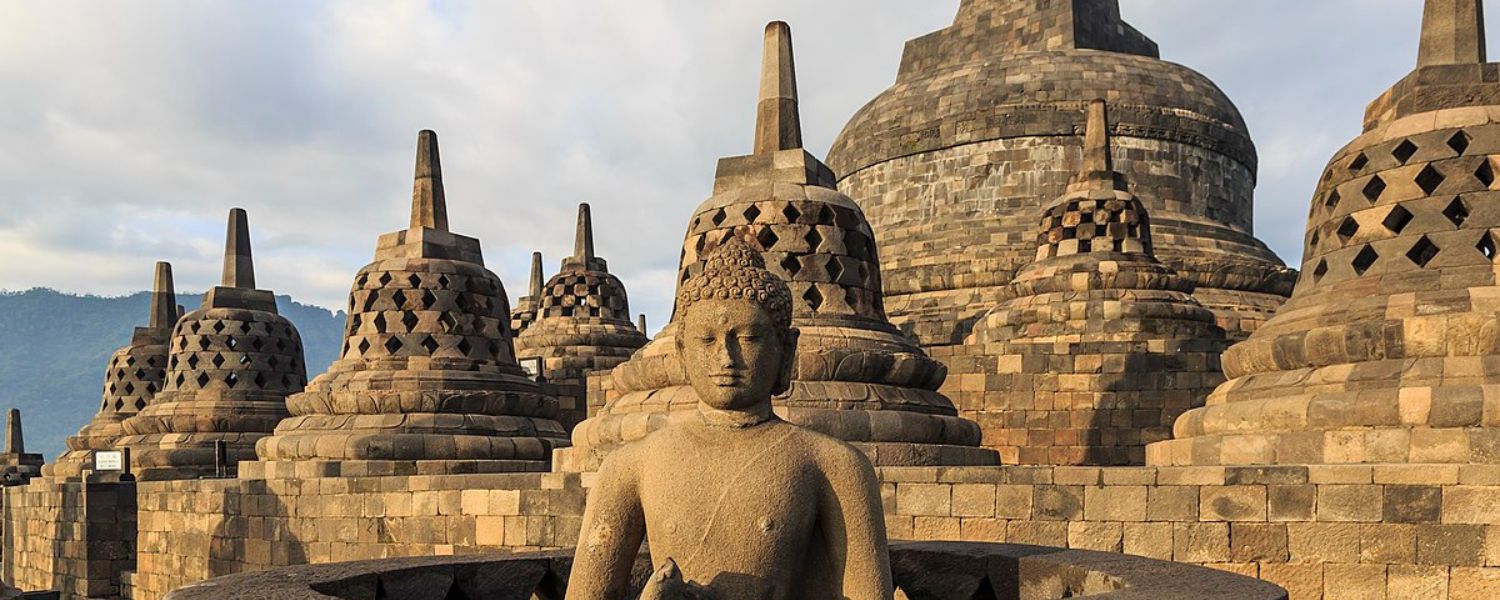

Buddhist architecture of India is characterized by stupas, monasteries, and rock-cut caves, reflecting the spread and influence of Buddhism.
The Ajanta and Ellora Caves are examples of remarkable rock-cut architecture adorned with intricate sculptures and murals depicting Buddhist teachings and narratives.
4. Hindu Temple Architecture
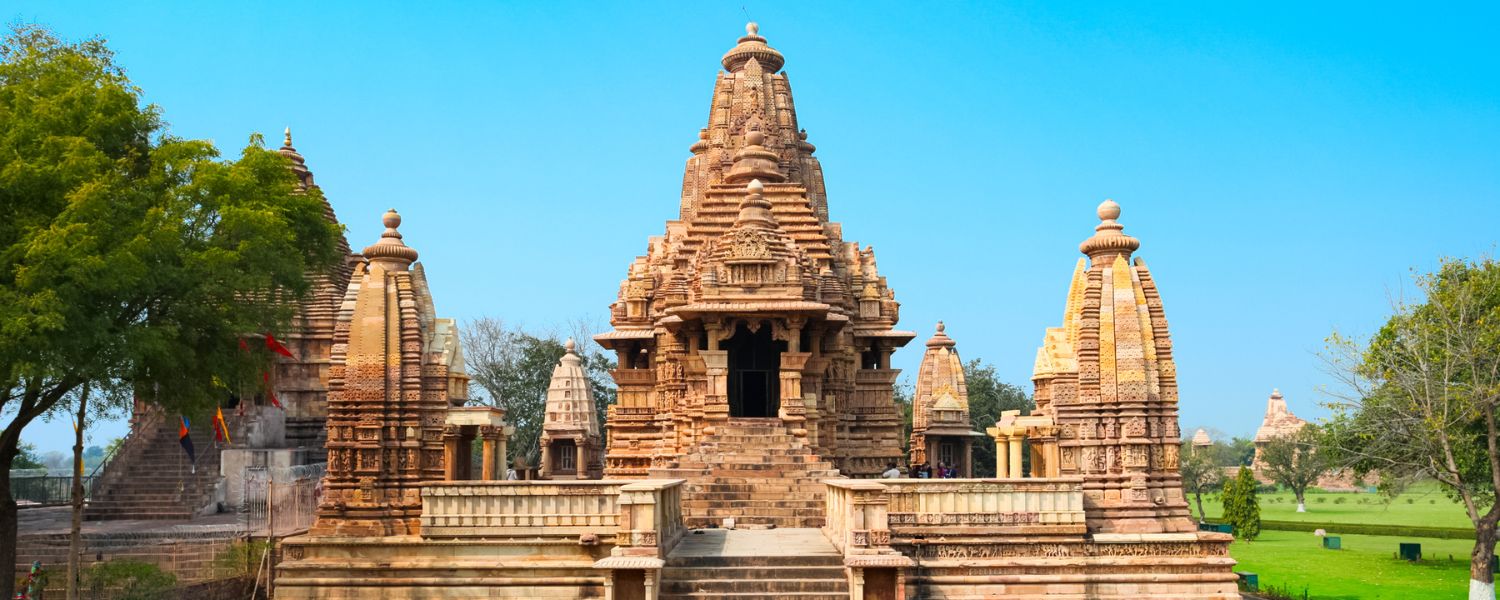

Hindu temple architecture of India is diverse and has evolved over centuries, reflecting regional styles and beliefs.
These temples are often characterized by intricate carvings, towering spires (shikhara), and elaborate entrance gateways (gopurams).
The Brihadeeswarar Temple in Thanjavur and the Khajuraho Temples exemplify detailed craftsmanship and spiritual symbolism.
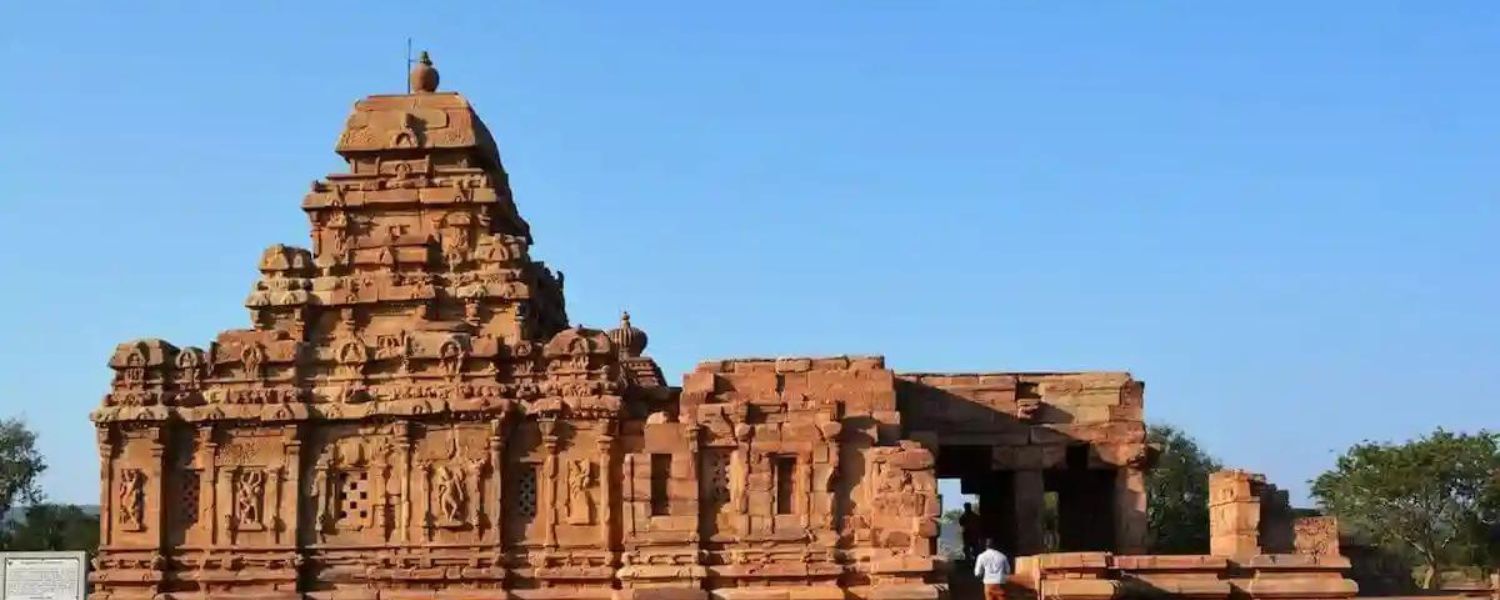
5. Gupta Architecture

Gupta architecture of India flourished during the Gupta Empire and is known for its structural mastery and aesthetic finesse.
The Dashavatara Temple in Deogarh and the Ajanta Caves exemplify the Gupta architecture of India with elaborate sculptures, refined ornamentation, and structural grandeur.
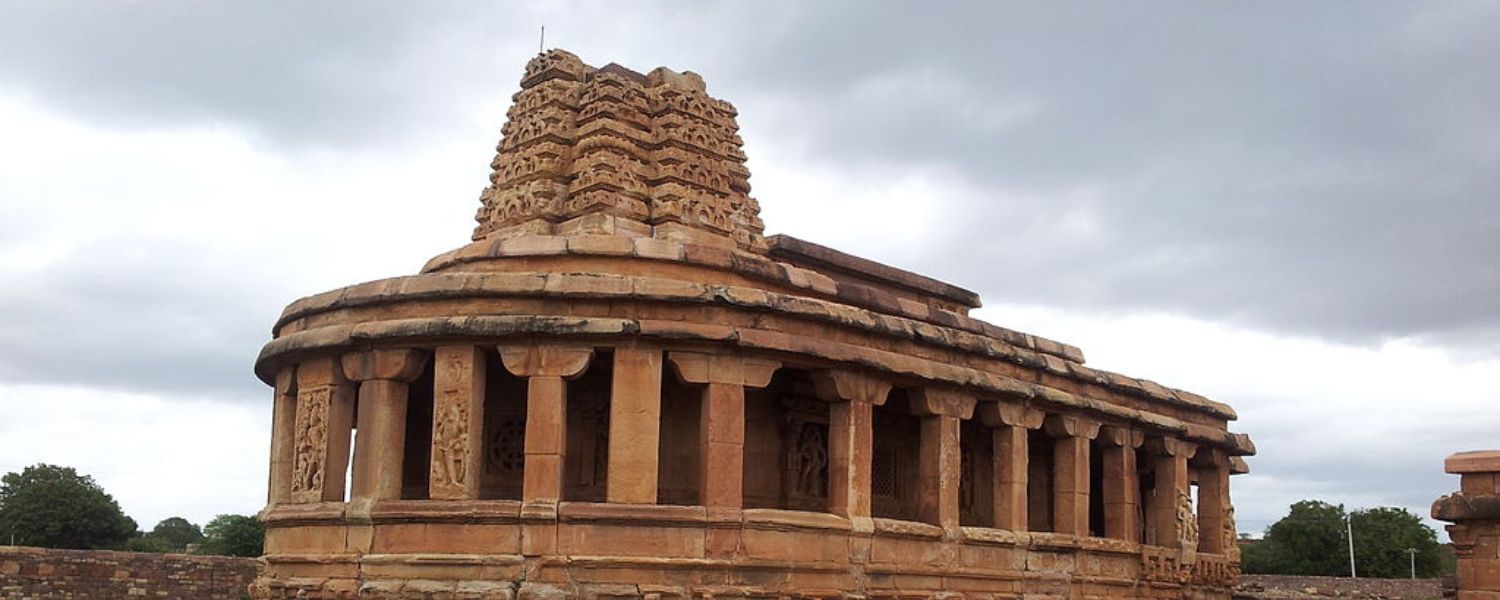
6. Chalukya Architecture

Chalukya architecture, prevalent in southern India, is characterized by intricately carved temples and monolithic structures.
The Virupaksha Temple in Pattadakal and the Mahakuta Group of Temples are prime examples, showcasing Dravidian and Nagara architectural styles with elaborate sculptures and towering vimanas.
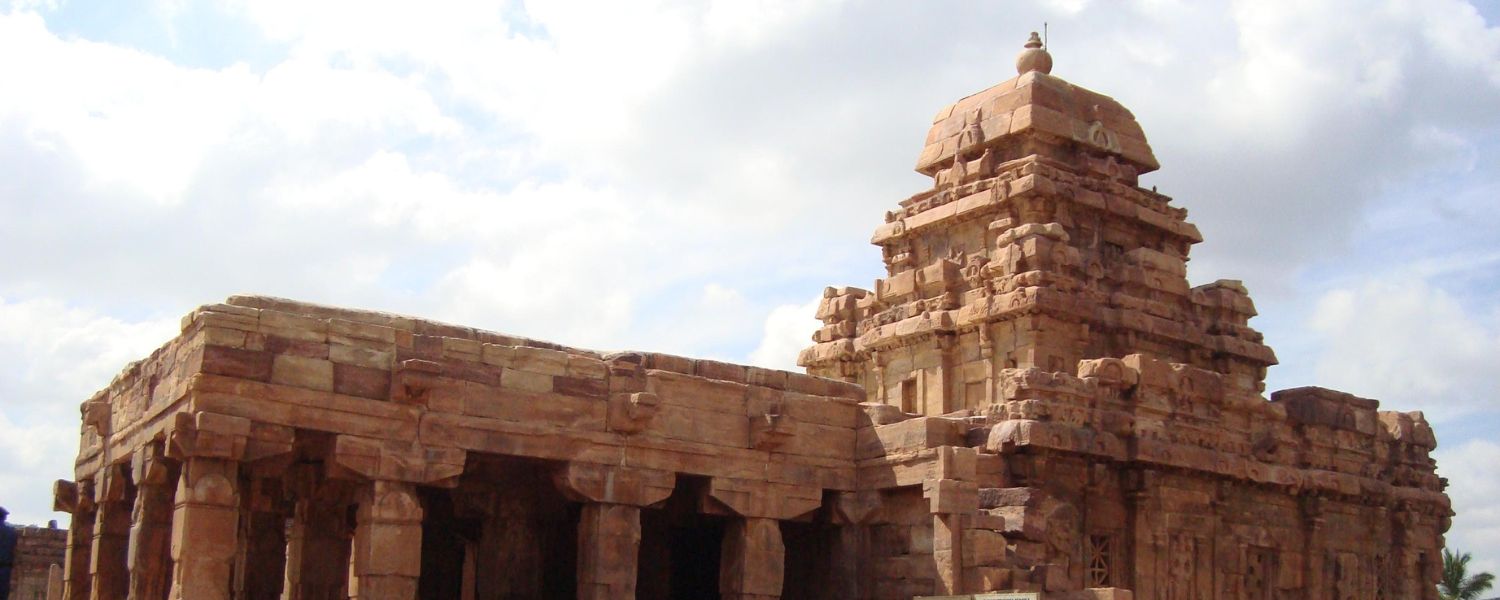
7. Rashtrakuta Architecture

Rashtrakuta architecture, during the Rashtrakuta dynasty, blended various regional styles, resulting in unique temple complexes.
The Kailasa Temple in Ellora carved out of a single rock, is a marvel of Rashtrakuta architecture, showcasing intricate carvings and elaborate architectural detailing.
8. Pallava Architecture
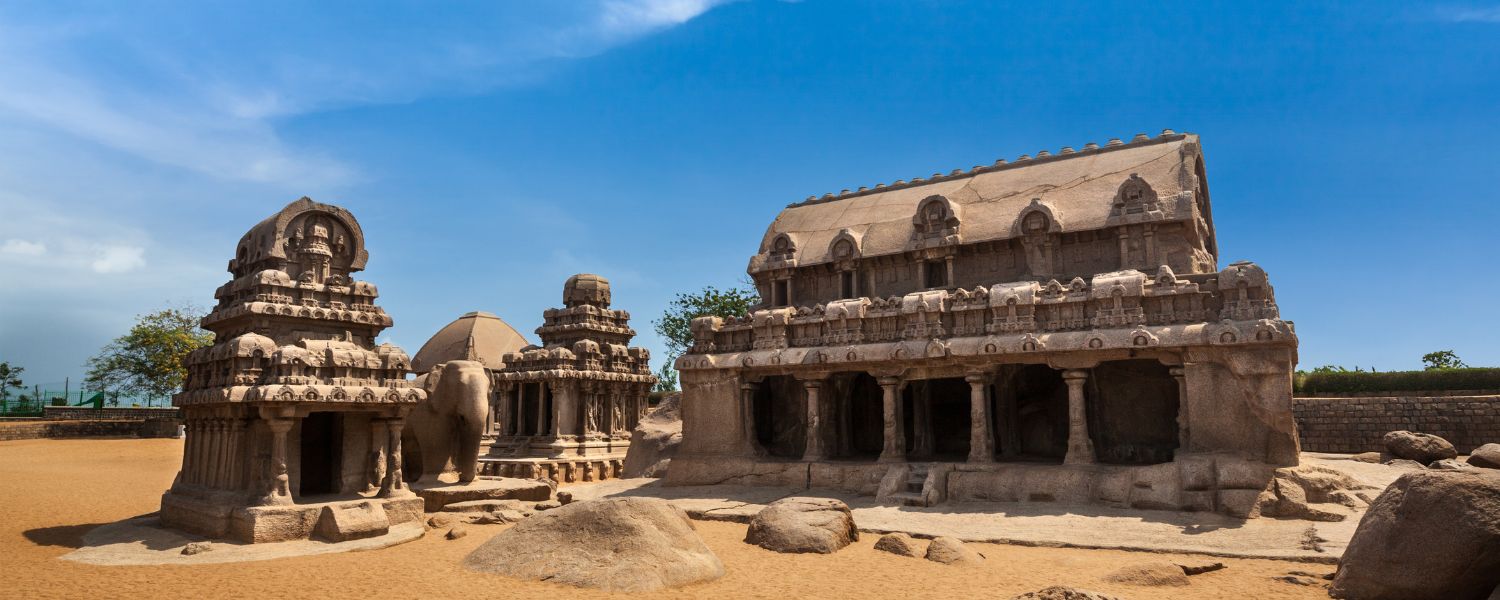

Pallava architecture, prominent in Tamil Nadu, is known for its rock-cut temples and monolithic rathas (chariot-shaped temples).
The Shore Temple in Mahabalipuram and the Kailasanatha Temple in Kanchipuram exemplify Pallava architecture, showcasing exquisite sculptures and intricate architectural details.
9. Chola Architecture
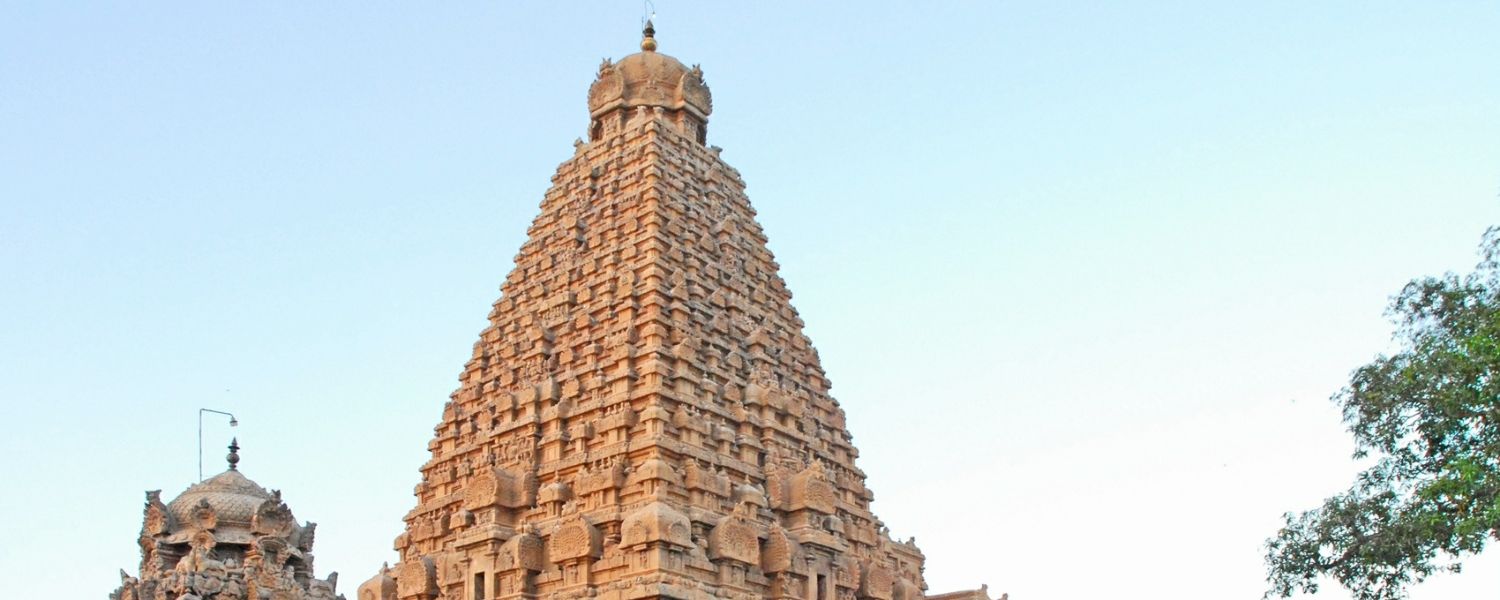

During the Chola dynasty, Chola architecture reached its zenith with the construction of magnificent temples adorned with intricate sculptures and towering vimanas.
The Brihadeeswarar Temple in Thanjavur, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is a masterpiece of Chola architecture, showcasing grandeur and architectural excellence.
10. Hoysala Architecture
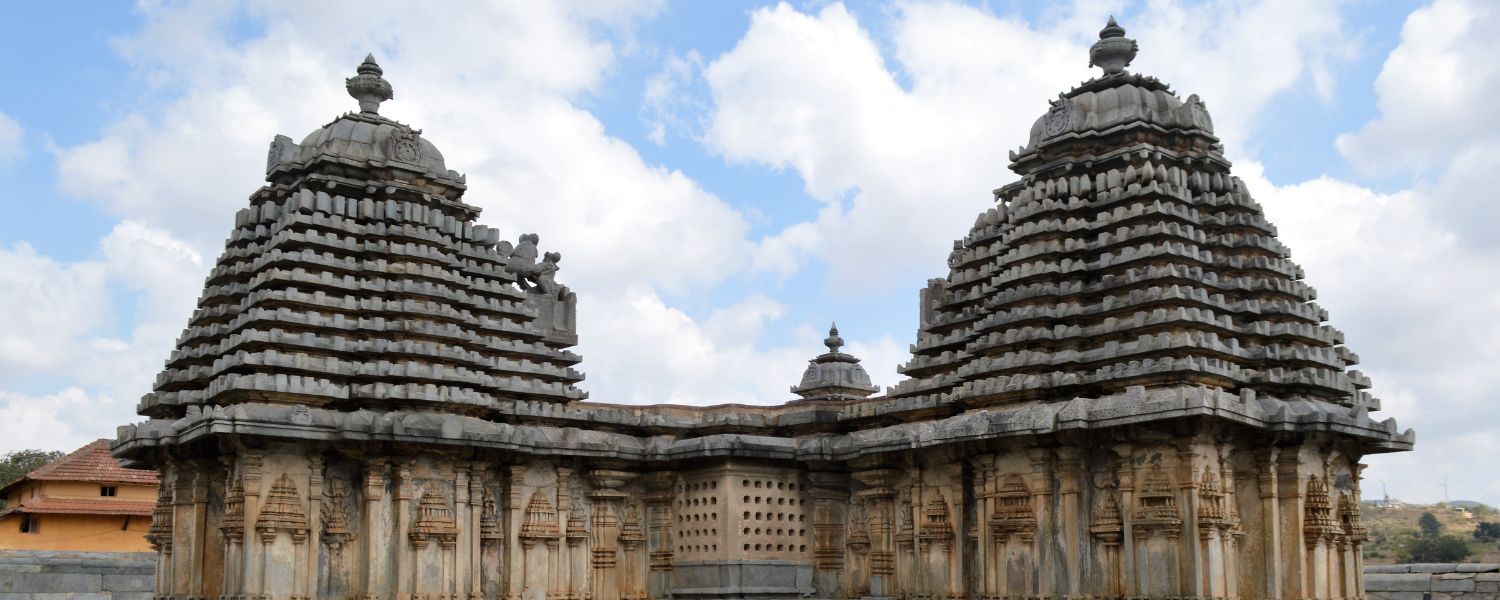

Hoysala architecture, prevalent in Karnataka, is renowned for its intricate craftsmanship and ornate sculptures.
The Chennakesava Temple in Belur and the Hoysaleswara Temple in Halebidu are prime examples, showcasing Hoysala architecture’s exquisite carvings and structural elegance.
11. Vijayanagara Architecture
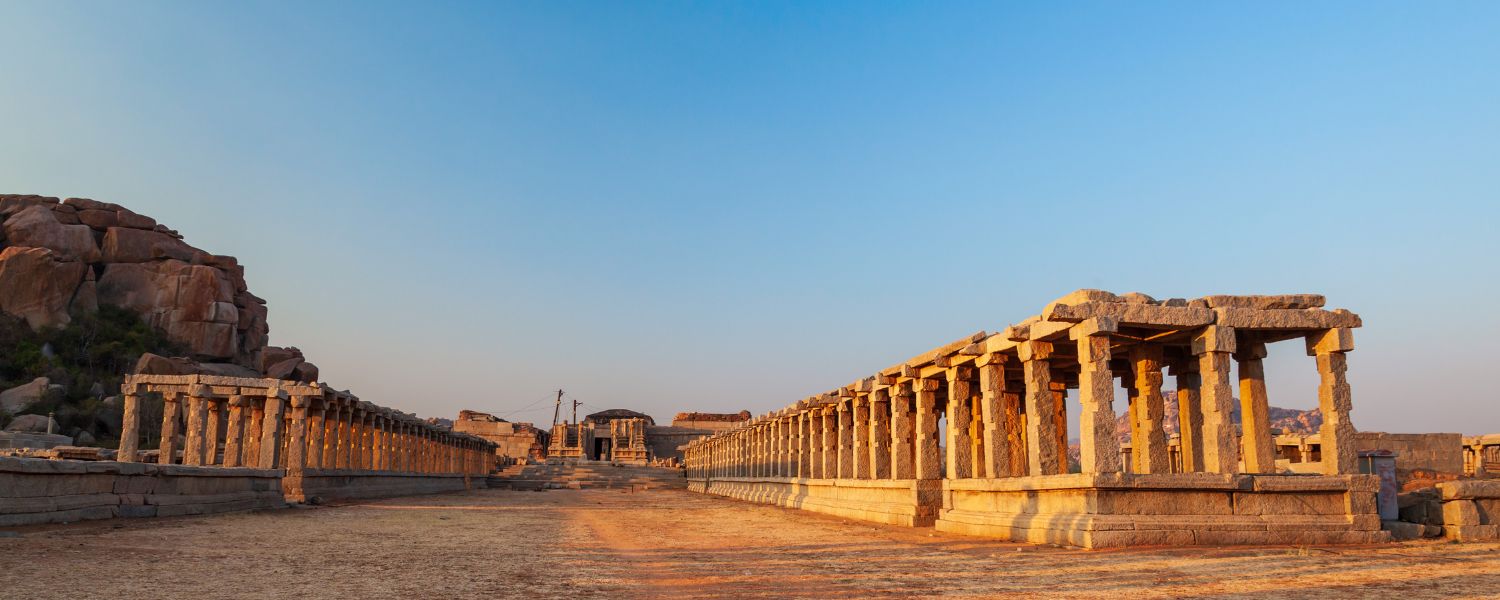

Vijayanagara architecture of India is a testament to the grandeur of the Vijayanagara Empire, showcasing a unique blend of Dravidian and Hoysala architectural styles.
Prominent features include ornate gopurams (gateways), intricately carved pillars, and monolithic sculptures.
Vijayanagara Architecture focused on creating monumental structures like temples, palaces, and administrative buildings, reflecting the empire’s religious and cultural ethos.
The architectural marvels of Hampi, including the Virupaksha Temple and Vittala Temple, are prime examples of this remarkable style.
12. Mughal Architecture
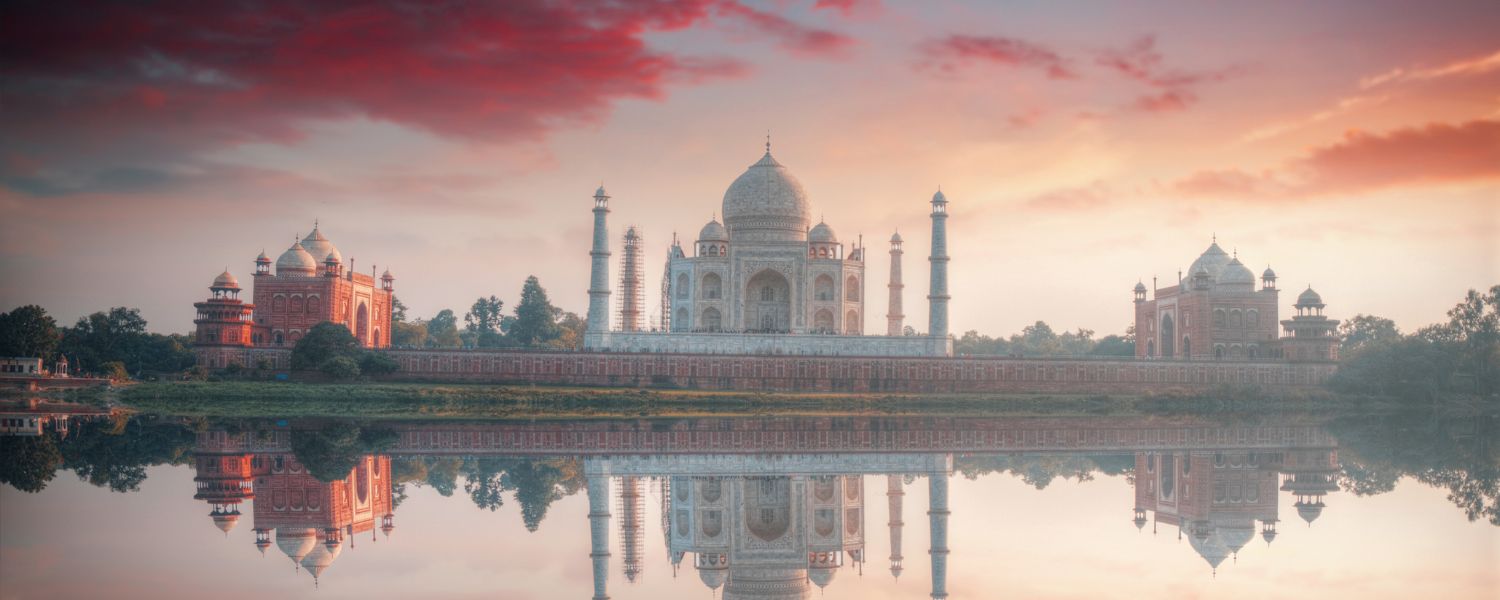

The Mughal architecture of India epitomizes the luxury and sophistication of the Mughal dynasty, characterized by grandeur, symmetry, and intricate ornamentation.
Notable features include bulbous domes, slender minarets, and symmetrical gardens.
Taj Mahal represents the pinnacle of Mughal Architecture, showcasing exquisite marble inlay work and perfect harmony in design.
13. Delhi Sultanate Architecture
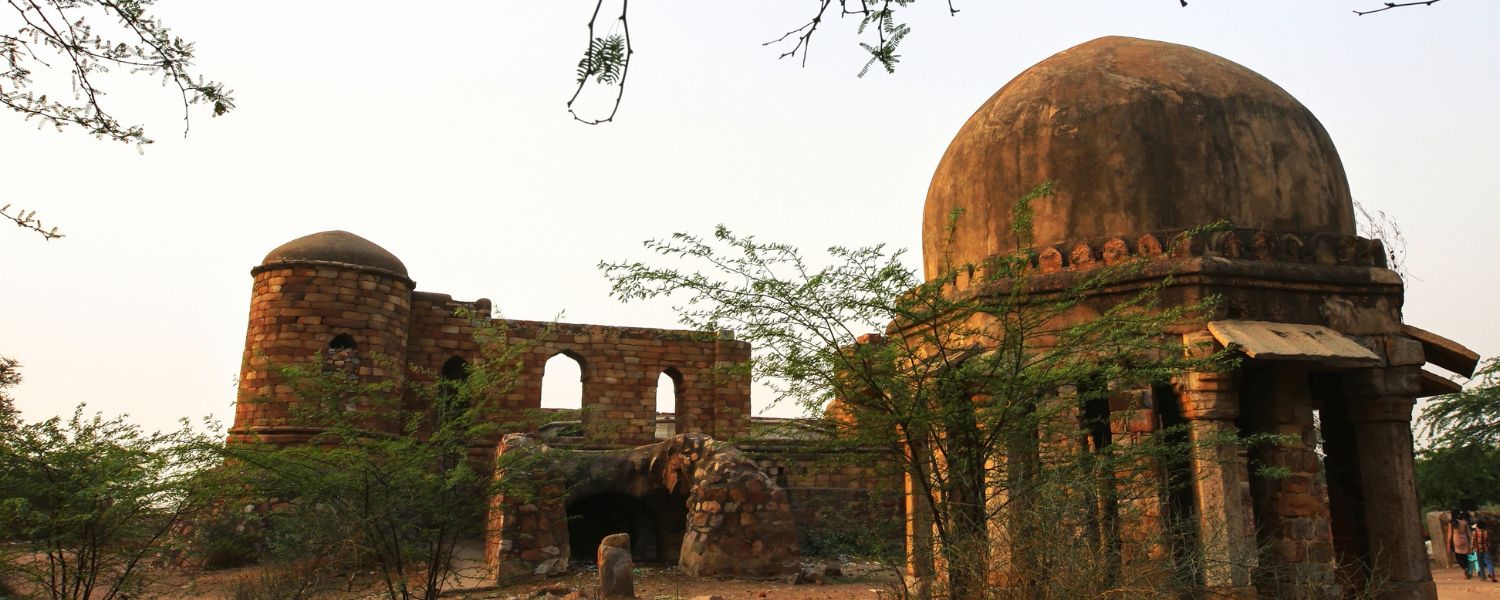

Delhi Sultanate Architecture reflects the fusion of Islamic and indigenous styles, marked by red sandstone, arches, and domes.
Fundamental structures such as the Qutub Minar and Alai Darwaza highlight the sultans’ architectural prowess, emphasizing religious and military significance.
14. Rajput Architecture

The Rajput architecture of India is characterized by its fortresses, palaces, and temples, which blend Rajput and Mughal influences.
Forts like Chittorgarh Fort and palaces like City Palace and Jaipur exhibit intricate carvings, vibrant frescoes, and imposing gateways, reflecting the courage and grandeur of Rajput rulers.
15. Maratha Architecture
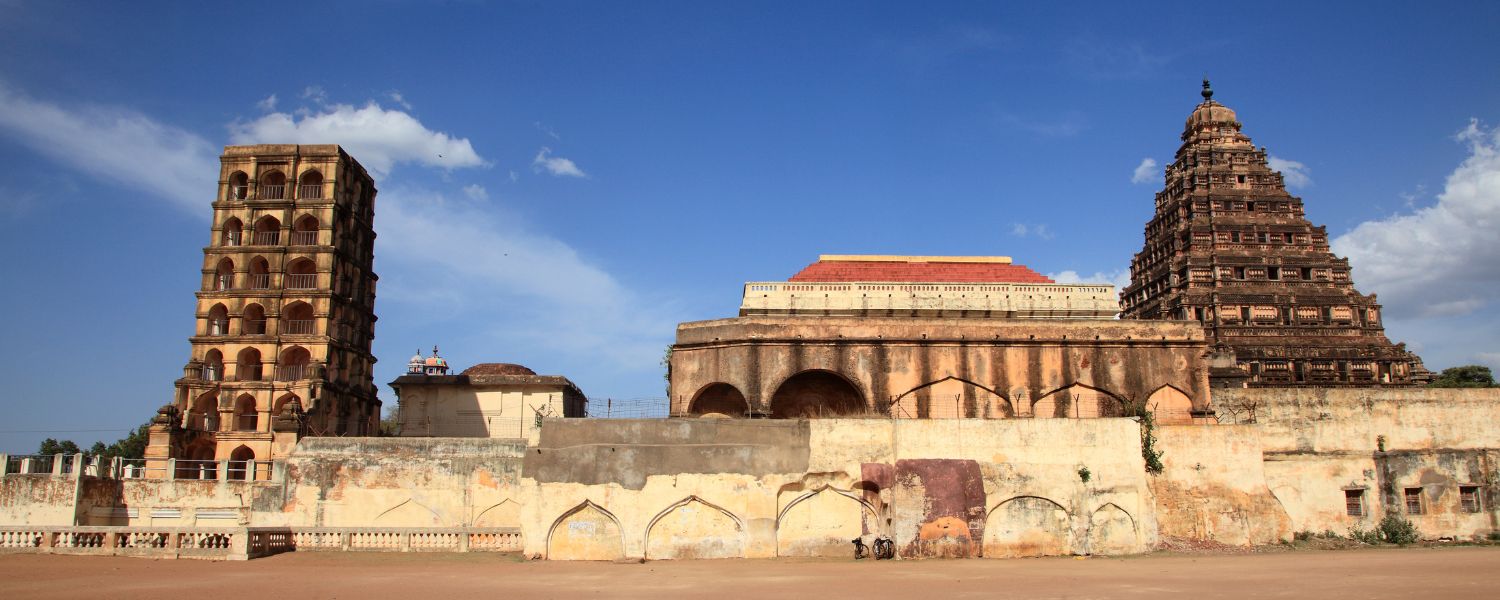

Maratha architecture of India is known for its sturdy fortifications and temple complexes, reflecting the military and religious ethos of the Maratha Empire.
Structures like Raigad Fort and Shaniwar Wada exemplify Maratha Architecture, featuring robust construction and minimal ornamentation.
16. Sikh Architecture
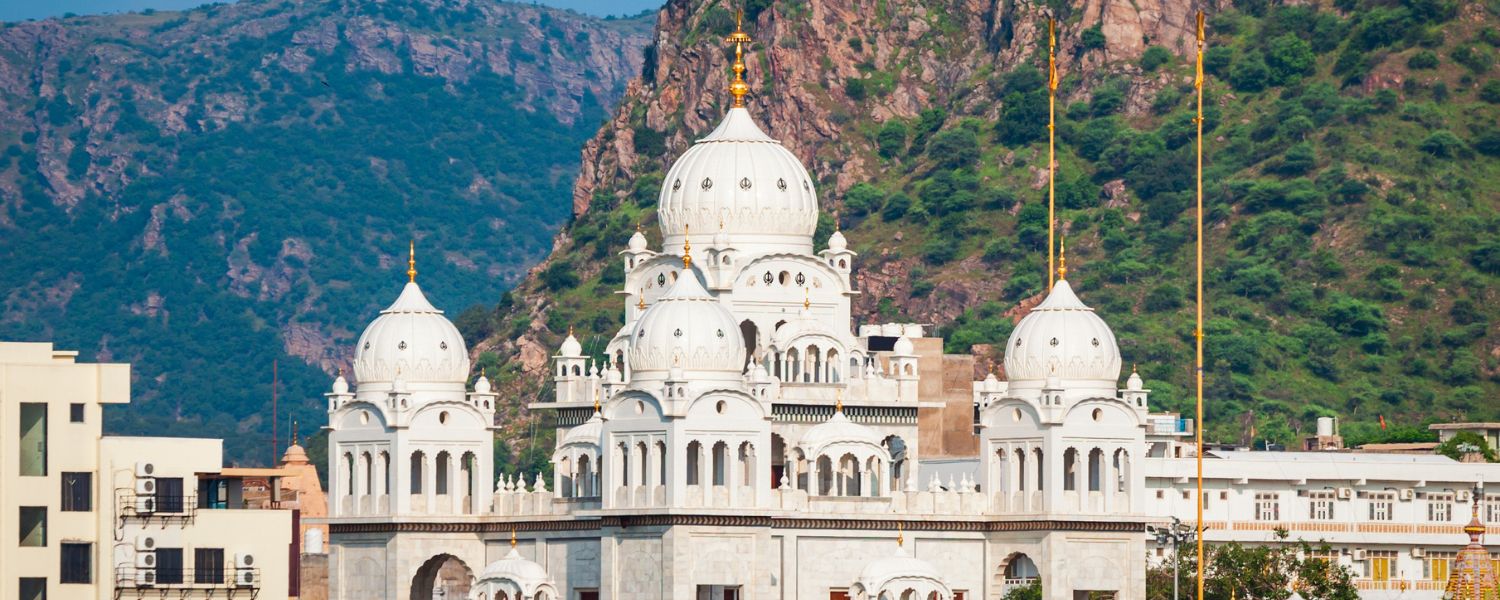

Sikh Architecture is characterized by its simplicity and spirituality, reflecting the egalitarian values of Sikhism.
The Golden Temple in Amritsar stands as the most revered example, with its distinctive gold-plated dome and serene Sarovar (sacred pool) embodying the essence of Sikh Architecture.
17. Deccan Sultanate Architecture
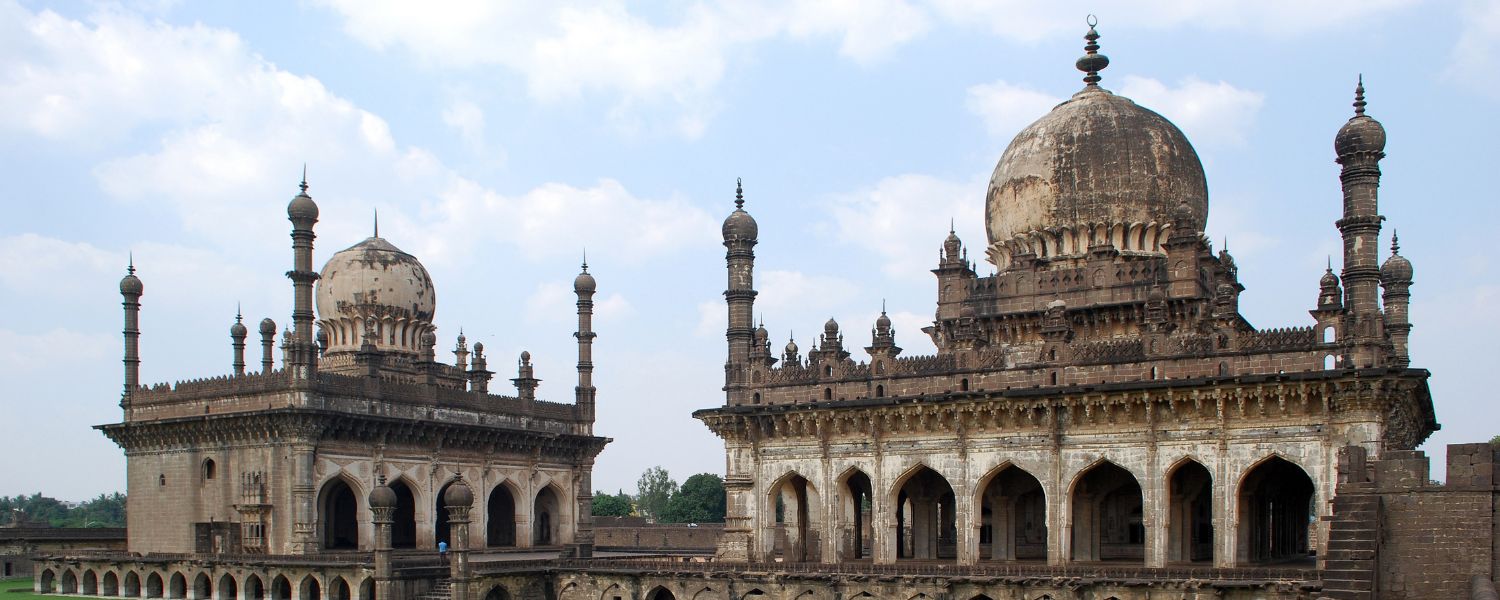

Deccan Sultanate Architecture showcases a unique amalgamation of Islamic, Hindu, and Persian styles, featuring grand mosques, tombs, and citadels.
The Gol Gumbaz in Bijapur, with its massive dome and whispering gallery, is a prime example of Deccan Sultanate Architecture, symbolizing power and architectural ingenuity.
18. Bahmani Sultanate Architecture
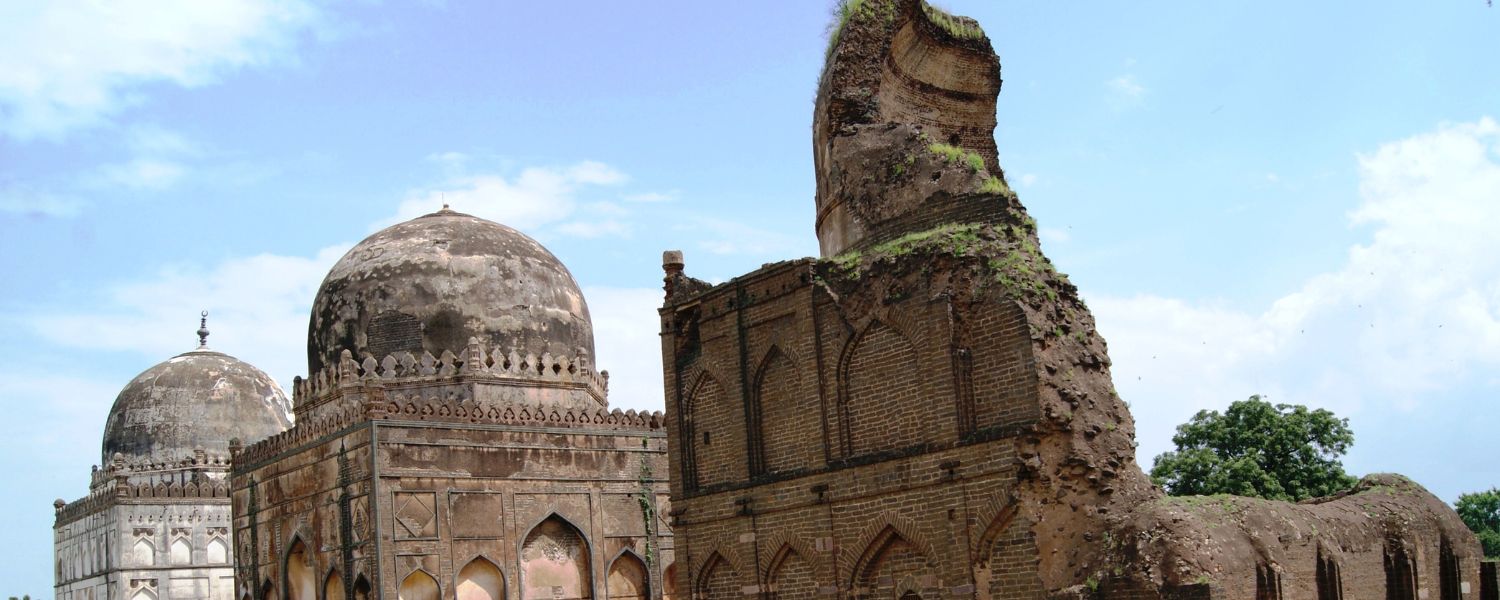

Bahmani Sultanate Architecture flourished in the Deccan region, characterized by its monumental structures and intricate decorations.
Notable examples include the Bidar Fort and the Bara Kaman mausoleum, reflecting the sultanate’s patronage of art and architecture.
19. Kashmiri Architecture
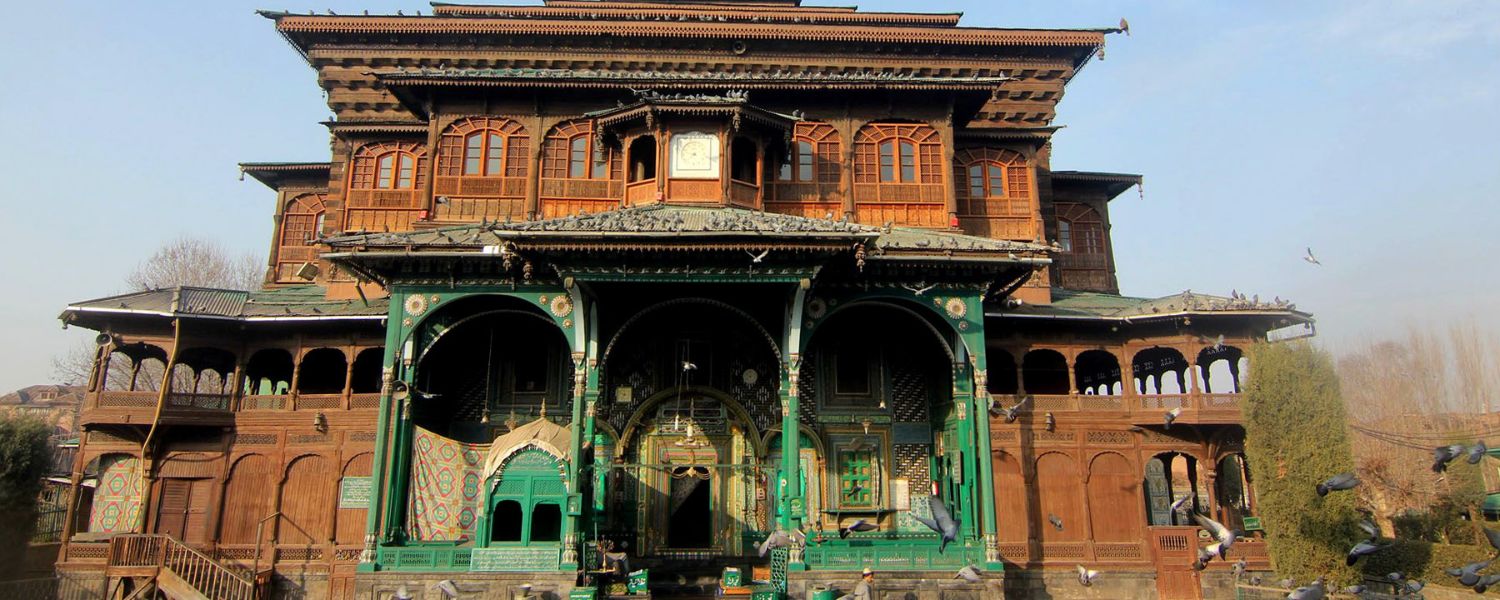

Kashmiri Architecture reflects the region’s natural beauty and cultural heritage, blending elements of Hindu, Buddhist, and Islamic styles.
The Shah Hamdan Mosque in Srinagar and the Martand Sun Temple exemplify Kashmiri Architecture with their wooden architecture, intricate carvings, and breathtaking landscapes.
20. Rajputana Architecture
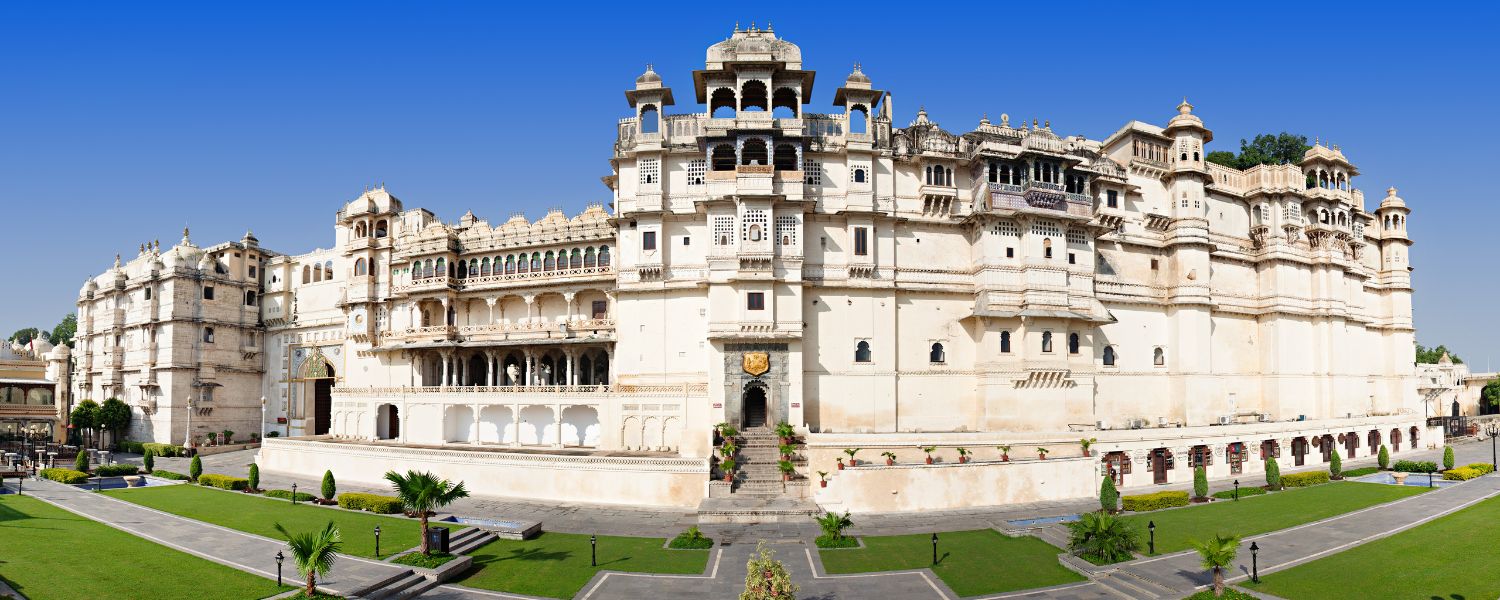

Rajputana architecture is a captivating blend of Hindu and Mughal styles that flourished in the erstwhile princely states of Rajasthan.
This architectural marvel showcases the courage and grandeur of the Rajput rulers. Characterized by ornate forts, intricately carved temples, and majestic palaces, Rajputana architecture reflects the opulence and splendor of the Rajput dynasty.
Each structure narrates tales of chivalry and romance, epitomizing the rich cultural heritage of India. Notable examples include the Amber Fort in Jaipur and Mehrangarh Fort in Jodhpur.
21. Maru-Gurjara Architecture
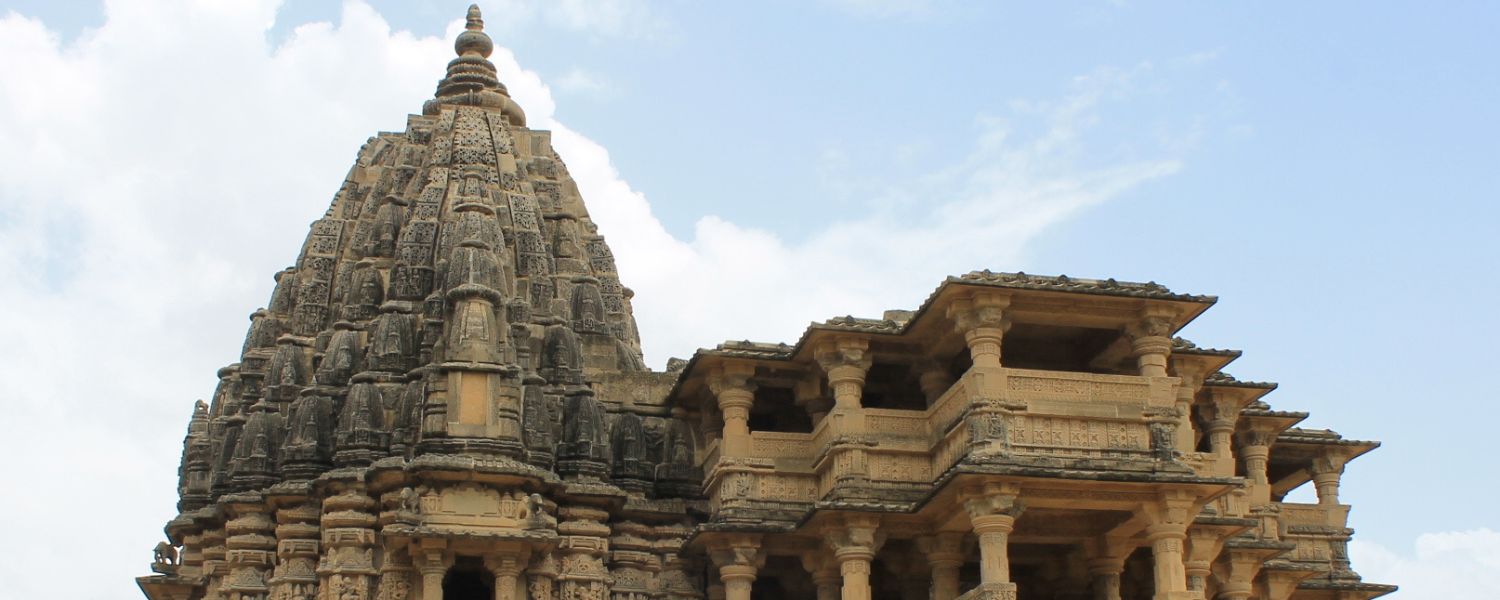

Maru-Gurjara architecture, synonymous with the architectural style prevalent in the western regions of India, particularly Gujarat and Rajasthan, is a testament to the creative prowess of ancient artisans.
Hindu and Jain ideologies influence this style, which features exquisite craftsmanship, intricate carvings, and elaborate ornamentation.
The iconic step-wells (baolis), intricate temples like the Dilwara Temples in Mount Abu, and grand palaces exemplify the grandeur of Maru-Gurjara architecture.
22. Kerala Temple Architecture
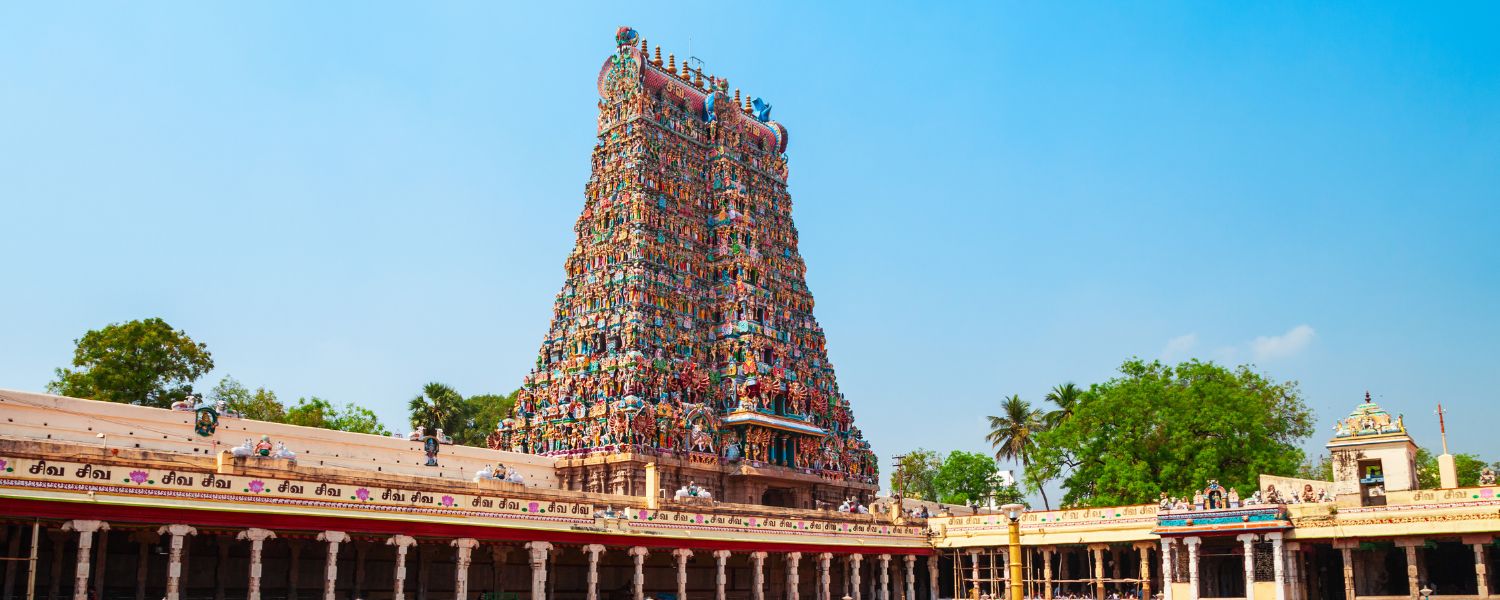

Kerala temple architecture, renowned for its distinctive style and intricate craftsmanship, is a hallmark of the state’s rich cultural heritage.
Influenced by Dravidian and indigenous styles, Kerala temples boast intricate wooden carvings, gabled roofs, and towering gopurams (entrance towers).
The Padmanabhaswamy Temple in Thiruvananthapuram and Guruvayur Temple in Thrissur are iconic examples of Kerala’s temple architecture, captivating visitors with their architectural splendor and spiritual ambiance.
23. Bengal Architecture
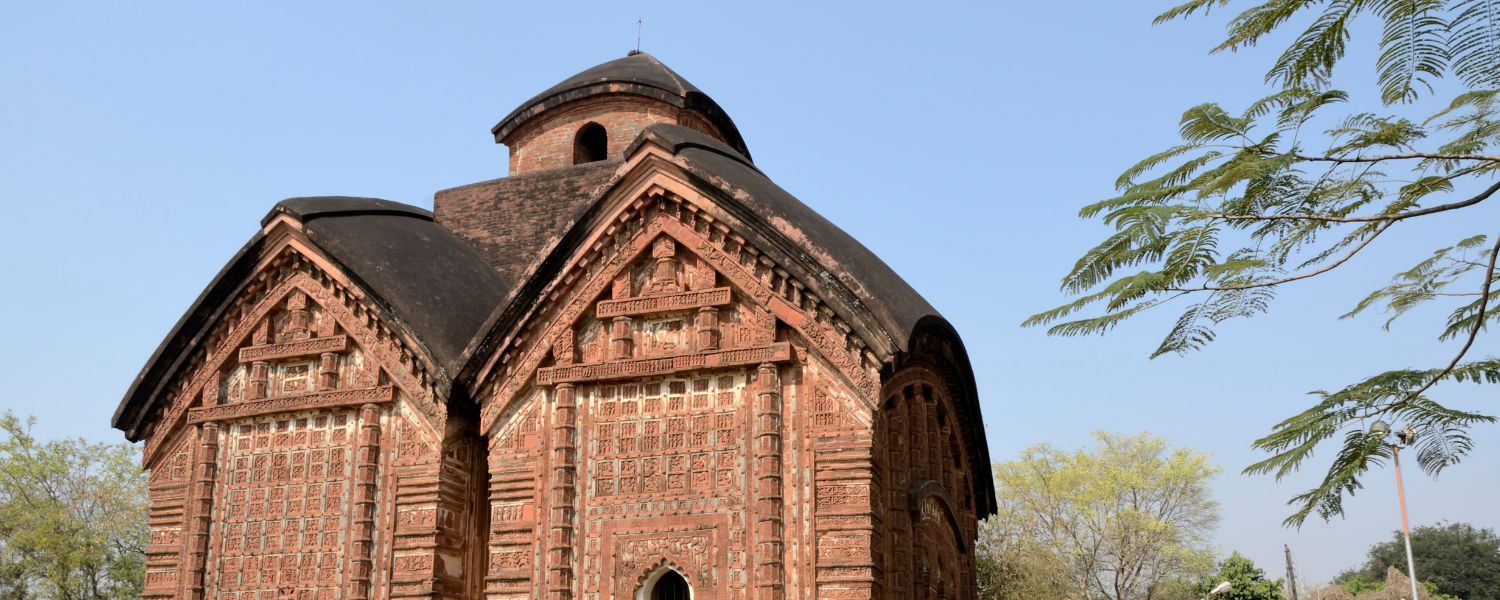

Bengal architecture, characterized by its unique blend of indigenous, Islamic, and European influences, is a testament to the region’s rich historical past.
Bengal’s architectural landscape is diverse and captivating, from terracotta temples adorned with intricate carvings to grand colonial buildings.
The Victoria Memorial in Kolkata and the ancient terracotta temples of Bishnupur exemplify Bengal’s rich architectural legacy, attracting admirers worldwide.
24. Orissan Architecture
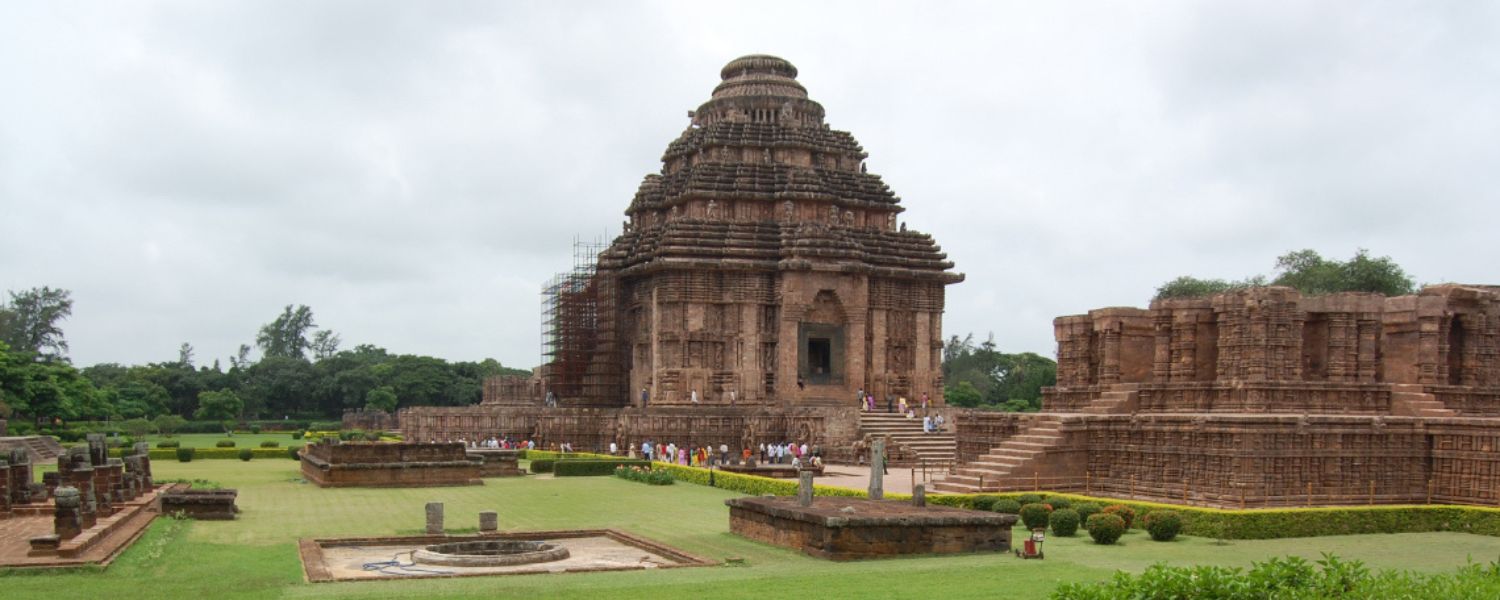

Orissan architecture, prevalent in the eastern state of Odisha, is renowned for its exquisite temples and intricate artwork.
Influenced by Hindu, Buddhist, and Jain traditions, Orissan temples feature towering spires (shikhara), intricately carved sculptures, and elaborate entrance gates.
The Sun Temple in Konark and the Jagannath Temple in Puri are prime examples of Orissan architecture, showcasing the region’s rich cultural and artistic heritage.
25. Indo-Islamic Architecture
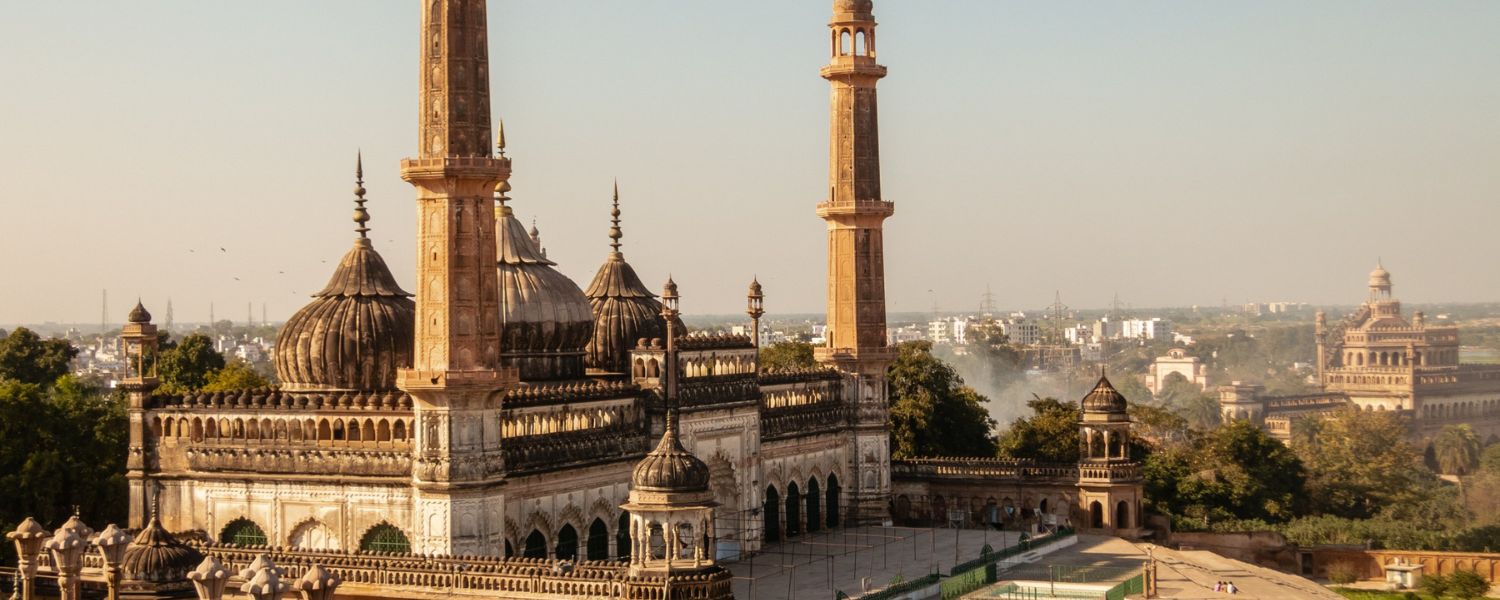

Indo-Islamic architecture, a fusion of Indian and Islamic architectural styles, flourished during the medieval period under various dynasties like the Delhi Sultanate and the Mughal Empire.
Characterized by grand mosques, minarets, intricate calligraphy, and ornate domes, Indo-Islamic architecture reflects the syncretic culture of India.
Iconic structures such as the Jama Masjid in Delhi and the Taj Mahal in Agra exemplify the magnificence of Indo-Islamic architecture, serving as enduring symbols of India’s cultural diversity.
26. Sikhara Style Architecture
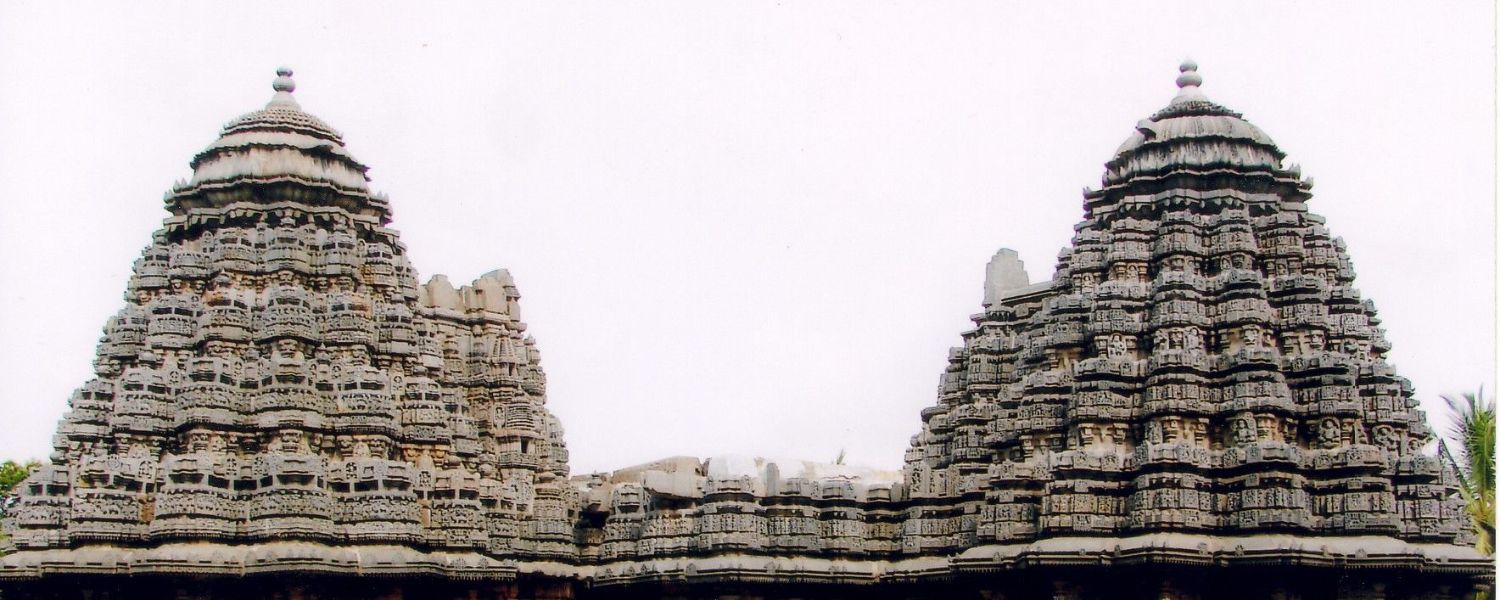

Sikhara style architecture, prevalent in North India, particularly in temple construction, is characterized by its towering spires (sikhara) adorned with intricate carvings and sculptures.
This architectural style is often associated with Hindu temples, where the sikhara symbolizes the sacred mountain Meru, the abode of the gods.
Temples like the Kandariya Mahadeva Temple in Khajuraho exemplify the elegance and grandeur of Shikhara-style architecture, captivating visitors with their divine beauty.
27. Nagara Style Architecture
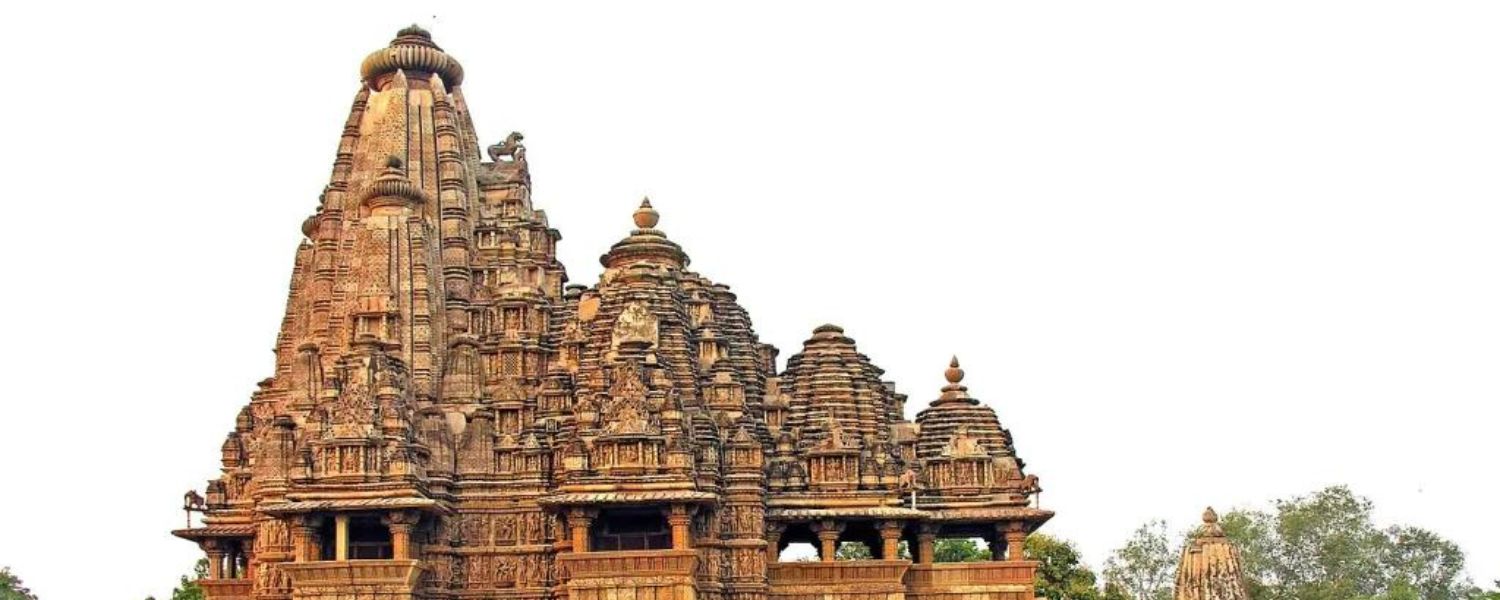

In Northern India, Nagara-style architecture is characterized by its tall and curvilinear spires (shikhara), intricate carvings, and elaborate entrance gates (toranas).
This style is predominantly seen in Hindu temples and is symbolic of Mount Meru, the mythical abode of the gods.
The Kashi Vishwanath Temple in Varanasi and the Badrinath Temple in Uttarakhand are prime examples of Nagara-style architecture, reflecting ancient India’s spiritual essence and architectural brilliance.
28. Dravidian Style Architecture
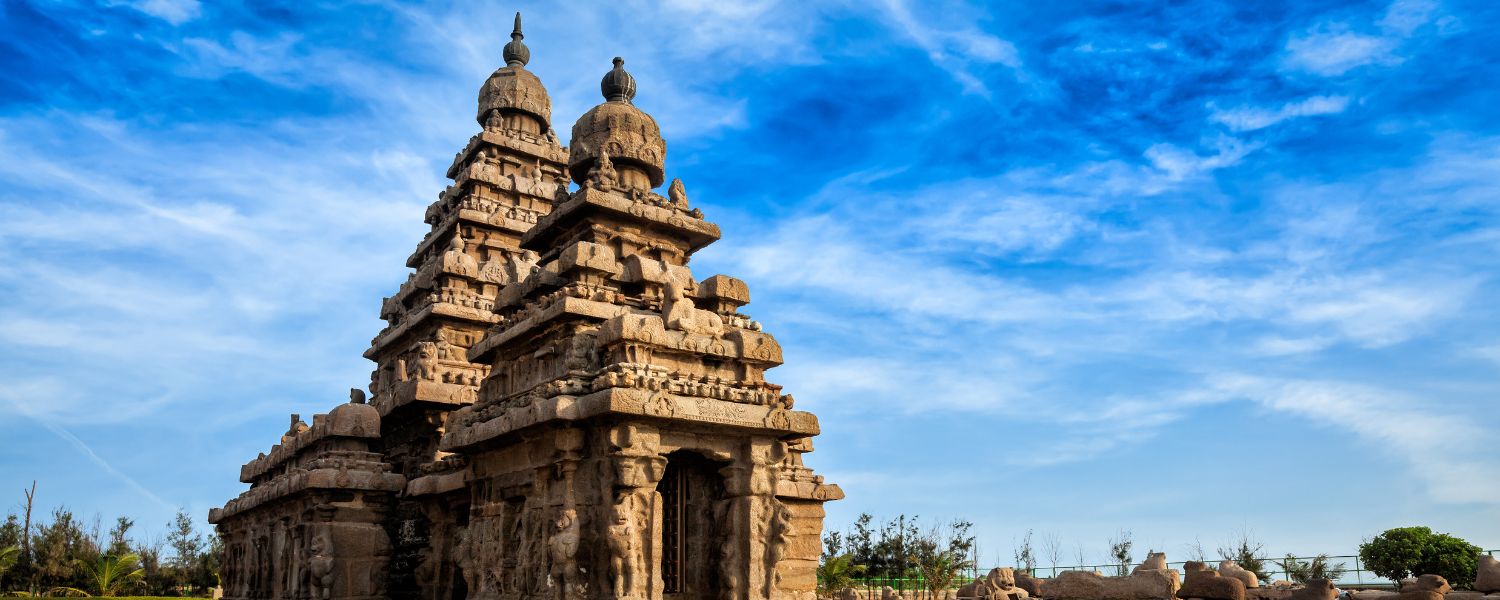

Dravidian style architecture, predominantly found in South India, is renowned for its majestic temple complexes, towering gopurams (entrance towers), and intricate sculptures.
Characterized by its pyramidal spires (vimanas), pillared halls, and vast temple courtyards, Dravidian temples exude grandeur and spirituality.
The Brihadeeswarar Temple in Thanjavur and the Meenakshi Temple in Madurai are iconic examples of Dravidian architecture, showcasing the rich cultural heritage of South India.
29. Vesara Style Architecture
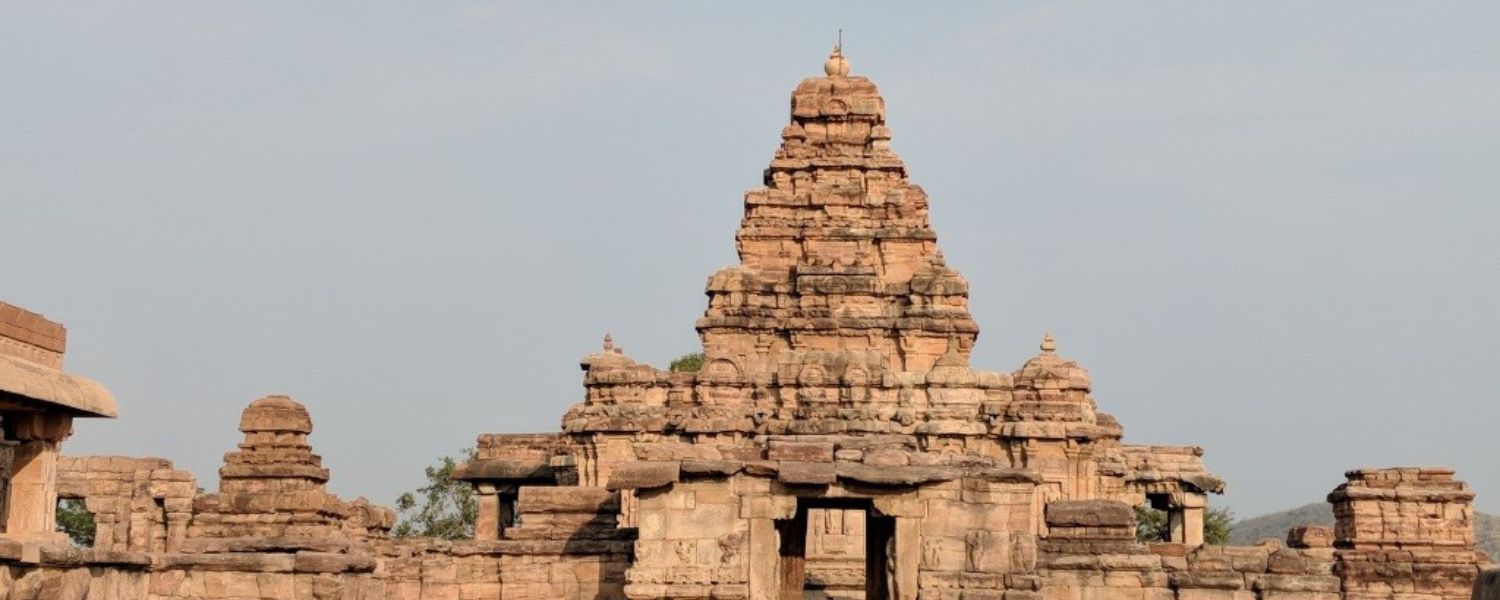

Vesara style architecture, also known as Chalukyan architecture, is a harmonious blend of Dravidian and Nagara styles that flourished in Central and Western India during the medieval period.
Characterized by intricately carved pillars, ornate sculptures, and tiered towers, the Vesara architecture of India reflects the cultural synthesis of different regions.
The temples of Ellora and Elephanta Caves exemplify the exquisite beauty and architectural ingenuity of the Vesara style, showcasing India’s rich heritage of artistic expression.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the architecture of India stands to the city’s rich history, diverse cultures, and architectural evolution over the centuries.
Kolkata’s architectural landscape blends past and present, from the majestic colonial buildings reflecting British influence to the intricate designs of Hindu temples showcasing indigenous craftsmanship.
Exploring the city’s architecture of India is like embarking on a journey through time, where each structure tells a unique story.
Whether the iconic Howrah Bridge symbolizes modern engineering marvels or the serene Victoria Memorial encapsulates colonial grandeur, every building contributes to Kolkata’s vibrant tapestry of architectural heritage.
FAQ
What are some famous architectural landmarks in Kolkata?
Kolkata boasts a rich tapestry of architectural marvels, including the iconic Victoria Memorial, the majestic Howrah Bridge, and the stunning Marble Palace. These landmarks reflect Kolkata’s diverse history and cultural heritage.
What architectural styles can be found in Kolkata?
Kolkata showcases a blend of architectural styles ranging from colonial to contemporary. You can find Victorian-era buildings in areas like Park Street, Art Deco influences in structures along Chowringhee Road, and traditional Bengali architecture of India in old mansions known as “thakur bari.”
Are there any must-visit architectural sites for history enthusiasts?
Absolutely! The Indian Museum, established in 1814, is one of the oldest museums in the world and showcases a remarkable collection of artifacts. Also, the Belur Math, designed to embody the harmony of religions, is a serene architectural gem worth exploring.
Can visitors explore Kolkata’s architectural heritage on foot?
Yes, indeed! Many of Kolkata’s architectural wonders are conveniently located within walking distance, particularly in areas like Esplanade and BBD Bagh. Guided walking tours are available for those keen on delving deeper into the city’s architectural legacy.